Wireless network performance
After many years of living (and testing) in the same apartment, I decided to move to a new place. Because of that, I can no longer use the comparison data I’ve collected about all the routers I’ve reviewed in the past. The new apartment is set up similarly to the diagram below. As you can see, I’ve placed the Xiaomi Mi Router AX1800 in a central position to provide good coverage in all the rooms where I tend to spend most of my time.
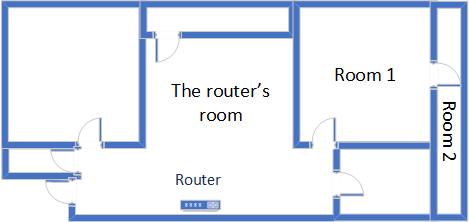
The apartment in which I tested Xiaomi Mi Router AX1800
I evaluated the quality of the wireless network managed by Xiaomi Mi Router AX1800 through measurements made in three different places:
- I record the maximum speeds when no walls absorb the wireless signal in the room where the router is placed.
- Room 1 - is separated by one wall from the router. So the wireless signal and the Wi-Fi speed I get should be lower here.
- Room 2 - is separated from the router by two walls absorbing the wireless signal. Also, the wall between Room 1 and Room 2 is twice as thick as the one between the router’s room and Room 1. I expect Room 2 to be a challenge for all the routers that I review, including this one.
I’ve made all my measurements using a brand new laptop that works great on Wi-Fi 6 networks, using Windows 11 and the latest drivers and operating system updates.
How the Xiaomi Mi Router AX1800 performs on the 2.4 GHz band
I always start my analysis by measuring the signal strength using NetSpot. When using the Wi-Fi 4 standard on the 2.4 GHz band, I was happy with the signal strength provided by the Xiaomi Mi Router AX1800 in all rooms.
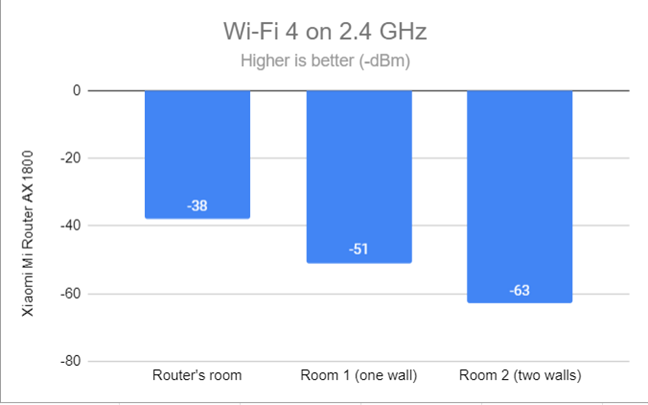
Signal strength on Wi-Fi 4 (2.4 GHz band)
However, when switching to the Wi-Fi 6 standard, the signal strength decreased significantly in the room furthest from the router.
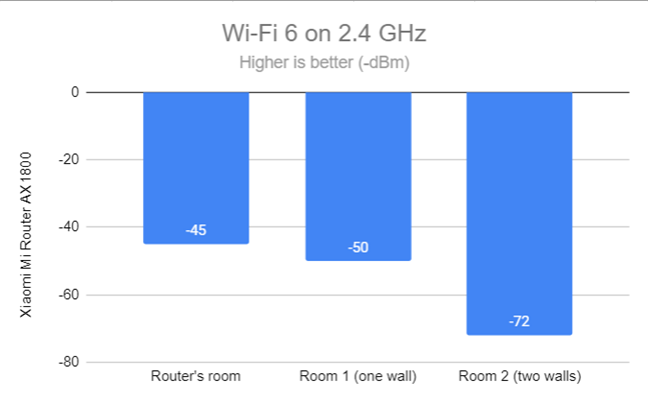
Signal strength on Wi-Fi 6 (2.4 GHz band)
I then used SpeedTest to see how fast the internet connection is on the 2.4 GHz band. When using Wi-Fi 4, Xiaomi Mi Router AX1800 performed reasonably well, but other AX1800 can provide faster downloads.
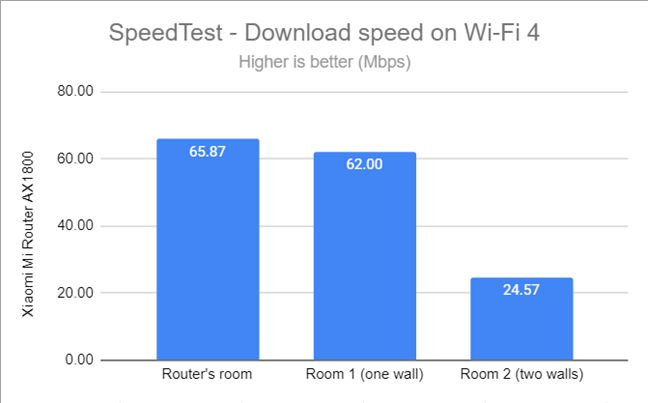
SpeedTest - The download speed on Wi-Fi 4 (2.4 GHz)
When measuring the upload speed, I noticed that in Room 2, separated by two walls from the router, this router couldn’t deliver any stable data throughput.
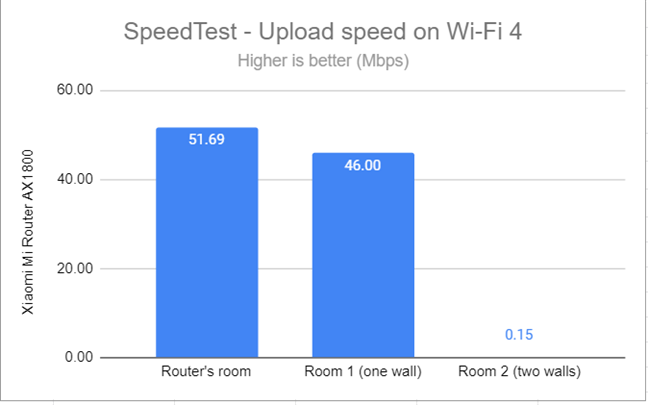
SpeedTest - The upload speed on Wi-Fi 4 (2.4 GHz)
Switching to Wi-Fi 6 on the 2.4 GHz band, I noticed faster downloads everywhere in my apartment. However, other AX1800 routers can deliver faster speeds than those shown below.
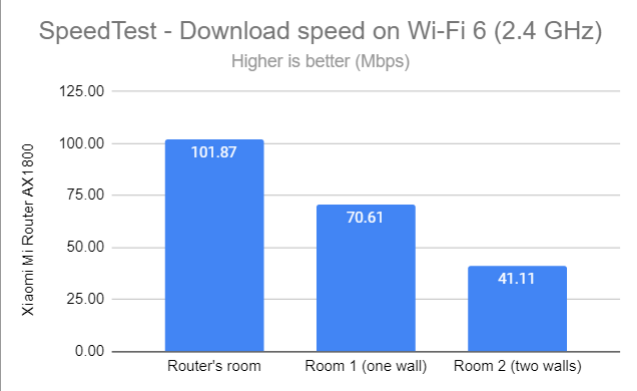
SpeedTest - The download speed on Wi-Fi 6 (2.4 GHz)
Things were slower in general when measuring the upload speed, and Room 2 was very problematic once again.
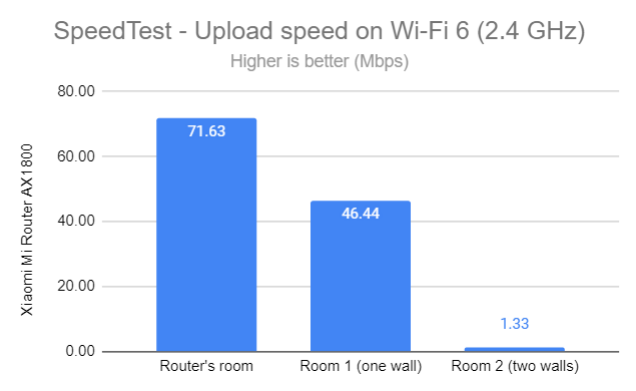
SpeedTest - The upload speed on Wi-Fi 6 (2.4 GHz)
For the next set of measurements, I used the PassMark Performance test to transfer data between two computers connected to the network on the 2.4 GHz band when using Wi-Fi 4. Again, downloads were reasonably fast, but I’ve seen better from other AX1800 routers.
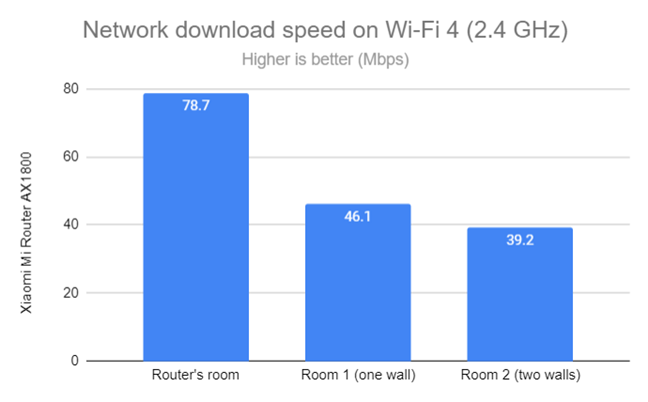
Network Wi-Fi downloads on Wi-Fi 4 (2.4 GHz)
When measuring the upload speed, I encountered the same issue in the room separated by two walls from the router.
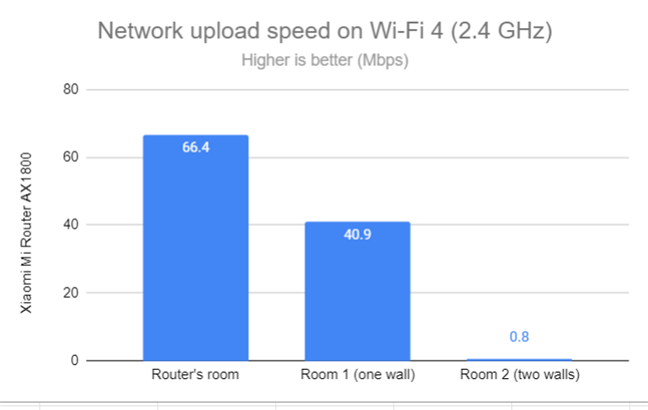
Network Wi-Fi uploads on Wi-Fi 4 (2.4 GHz)
I switched to the Wi-Fi 6 standard on the 2.4 GHz band and repeated the same measurements. I noticed a solid improvement in download speed in the room where the router is placed. However, in the other rooms, the speed improvements were barely noticeable.
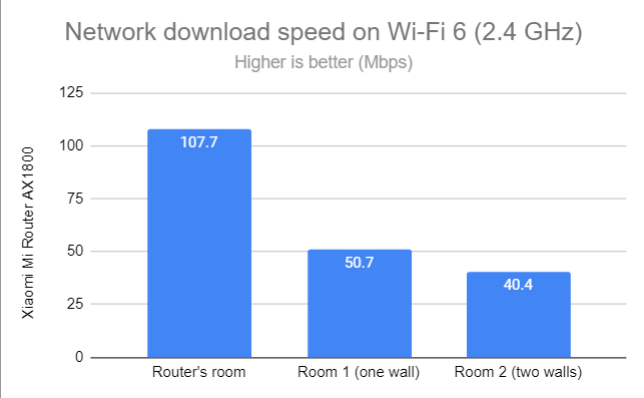
Network Wi-Fi downloads on Wi-Fi 6 (2.4 GHz)
Upload speeds were generally lower, and the router barely provided any throughput in Room 2.
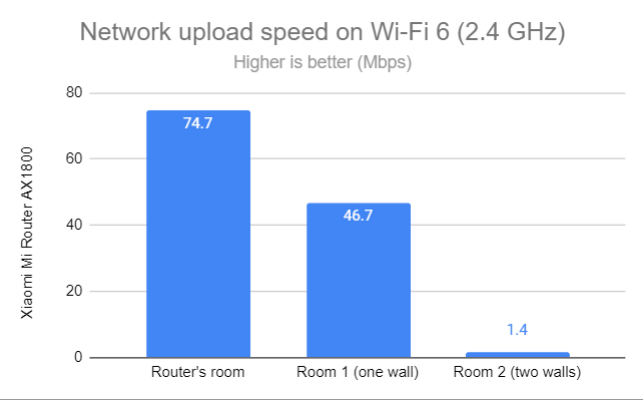
Network Wi-Fi uploads on Wi-Fi 6 (2.4 GHz)
My measurements have shown that Xiaomi Mi Router AX1800 can deliver reasonable speeds both on Wi-Fi 4 and Wi-Fi 6. However, this router doesn’t provide a large coverage area, and you shouldn’t be using it in large apartments.
How the Xiaomi Mi Router AX1800 performs on the 5 GHz band
I switched to the 5 GHz band, and I started by measuring the signal strength with NetSpot. When using the Wi-Fi 5 standard on the 5 GHz band, Xiaomi Mi Router AX1800 delivered solid signal strength, in line with what I’ve seen from other AX1800 routers.
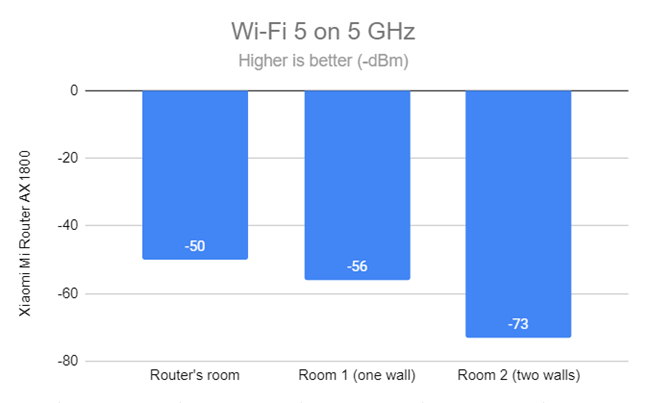
Signal strength on Wi-Fi 5 (5 GHz band)
When switching to Wi-Fi 6 on the 5 GHz band, the signal strength lowered slightly in all rooms.
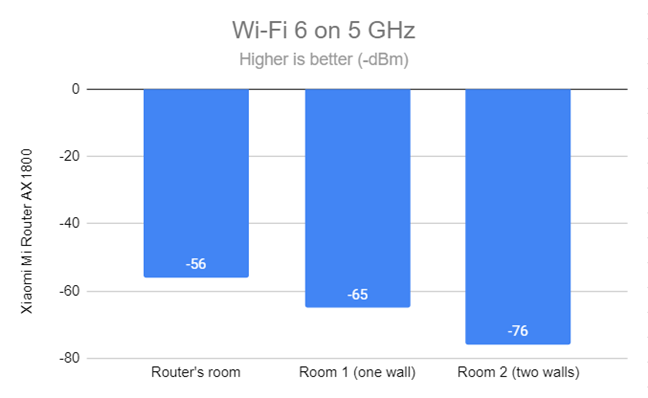
Signal strength on Wi-Fi 6 (5 GHz band)
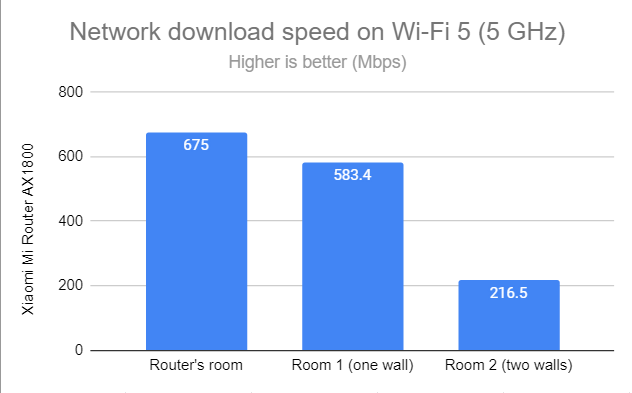
I then used SpeedTest to see how fast the internet connection is on the 5 GHz frequency band. When using the Wi-Fi 5 standard, Xiaomi Mi Router AX1800 delivered excellent download speeds in all rooms, including Room 2.
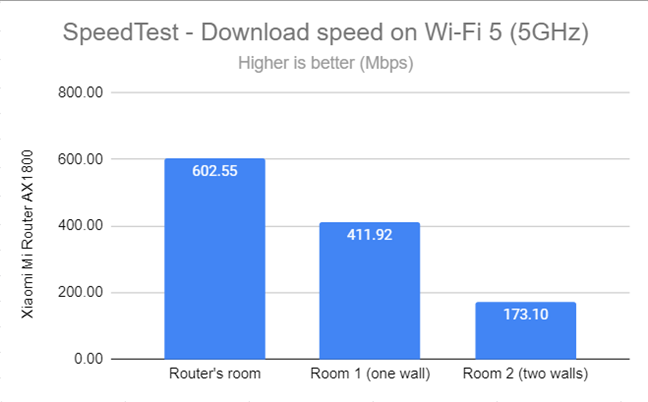
SpeedTest - The download speed on Wi-Fi 5 (5 GHz)
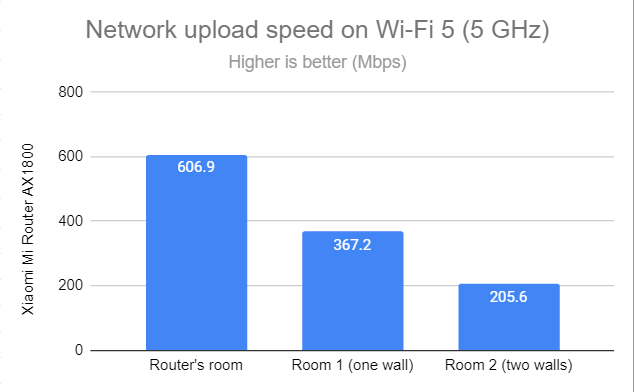
When measuring the upload, the speeds were even faster. An excellent result!
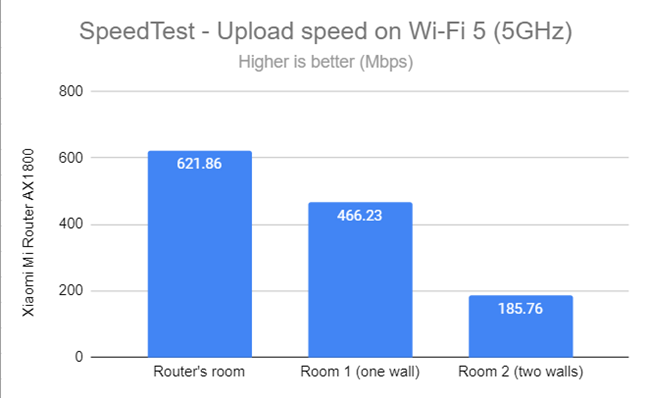
SpeedTest - The upload speed on Wi-Fi 5 (5 GHz)
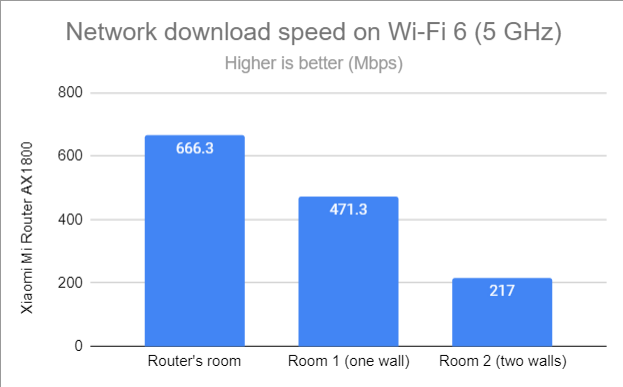
I changed from Wi-Fi 5 to Wi-Fi 6, and to my surprise, there were no meaningful improvements in download speeds. The differences were too minor to be noticeable.
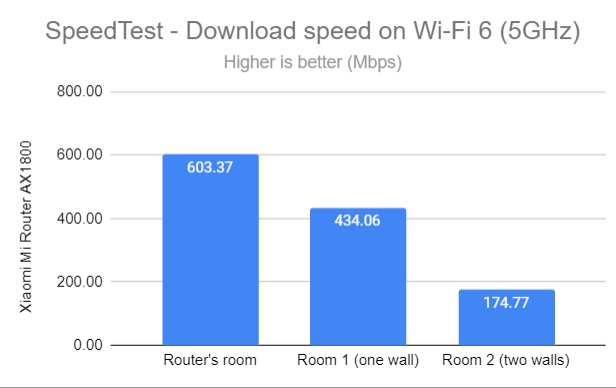
SpeedTest - The download speed on Wi-Fi 6 (5 GHz)
The same happened when measuring the upload speed too.
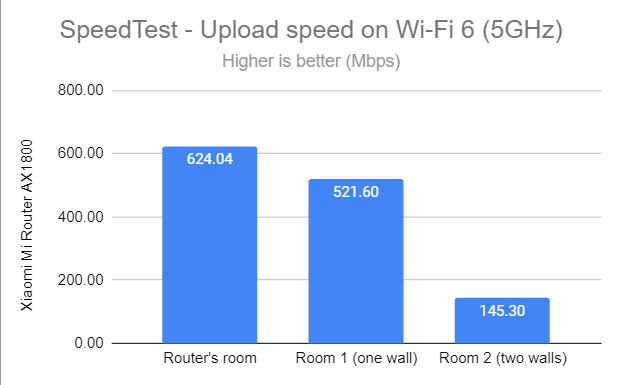
SpeedTest - The upload speed on Wi-Fi 6 (5 GHz)
For the next set of measurements, I used the PassMark Performance test to transfer data between two computers connected to the network on the 5 GHz band. Downloads were fast in all the rooms where I’ve made my measurements, and I was happy with the results.
Network Wi-Fi downloads on Wi-Fi 5 (5 GHz)
The same was true for the upload speed, including in Room 2.
Network Wi-Fi uploads on Wi-Fi 5 (5 GHz)
When switching to Wi-Fi 6, in some rooms, Xiaomi Mi Router AX1800 offers slower downloads than when using Wi-Fi 5.
Network Wi-Fi downloads on Wi-Fi 6 (5 GHz)
The same was valid for data uploads—a disappointing result.
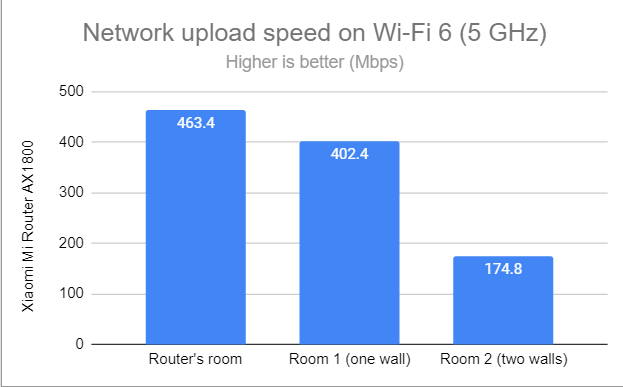
Network Wi-Fi uploads on Wi-Fi 6 (5 GHz)
My measurements have shown that Xiaomi Mi Router AX1800 can deliver excellent speeds using the Wi-Fi 5 standard. Unfortunately, switching to Wi-Fi 6 doesn’t deliver meaningful improvements, and, in some cases, the speed you get lowers. This is a problematic aspect that Xiaomi should fix in future firmware updates.
Wired network performance
It was time to evaluate the performance we get on Ethernet network connections. Our internet connection offers a maximum of 1 Gbps for the download speed and 800 Mbps for the upload.
When using SpeedTest, Xiaomi Mi Router AX1800 reached the maximum potential of our internet connection: 925.66 Mbps for the download and 788.06 Mbps for the upload.
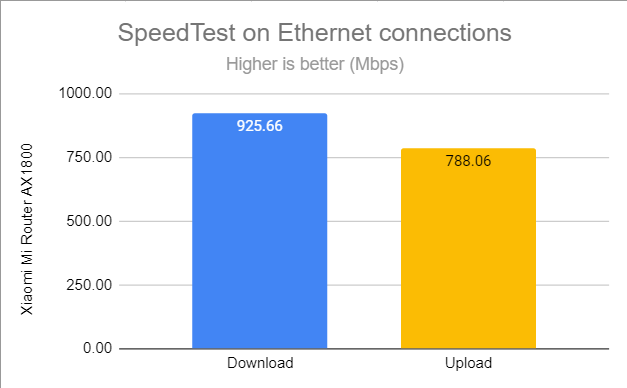
SpeedTest on wired connections
Ethernet connections work well on the Xiaomi Mi Router AX1800. Also, this router can use 1 Gbps internet connections to their maximum potential.
Extra features
The firmware on the Xiaomi Mi Router AX1800 is less complex than on competing routers from other brands. As a result, it doesn’t have as many advanced features as the competition does. What you get is the following:
- Wi-Fi Optimization - a feature that exists only in the Mi WiFi mobile app, not in the router’s web interface. It scans the signal strength of your network and the quality of your connection and it improves the router’s settings. I believe this should be added as a standard feature to the router’s firmware.
- Firewall - another mobile-only feature that makes it easy to evaluate the security of your network, set up blocklists for unwanted guests, and improve the password strength and WiFi security.
- IPv6 - nowadays, IPv6 compatibility is a must; it’s no longer counted as an “extra feature.” So this router can connect to the internet using IPv6 addresses, use IPv6 DNS servers, and assign IPv6 addresses to the clients that connect to its network.
- QoS - the router features an intelligent Quality of Service bandwidth allocation algorithm that prioritizes network traffic based on its type (gaming, web browsing, video, etc.). Unfortunately, it is designed to work only for 50 Mbps internet connections, rendering it unusable for people with fast internet connectivity of 100 Mbps and above.
- DDNS - a service that allows you to connect to the router from the internet, even if your internet provider assigns you a dynamic public IP address. Xiaomi Mi AX1800 can use the following DDNS services: Oray DDNS, PubYun, DynDNS, and No-IP.
- VPN - this router can connect to VPN services using the PPTP and L2TP protocols, but it cannot function as a VPN server. You also set which services or devices can use VPN traffic. However, many competing AX1800 routers can be set to work as VPN servers too.
- Mesh Wi-Fi - you can add the router as a node in a mesh Wi-Fi network composed of other Xiaomi wireless routers. It is a valuable feature when you need to increase the coverage of your Wi-Fi network.
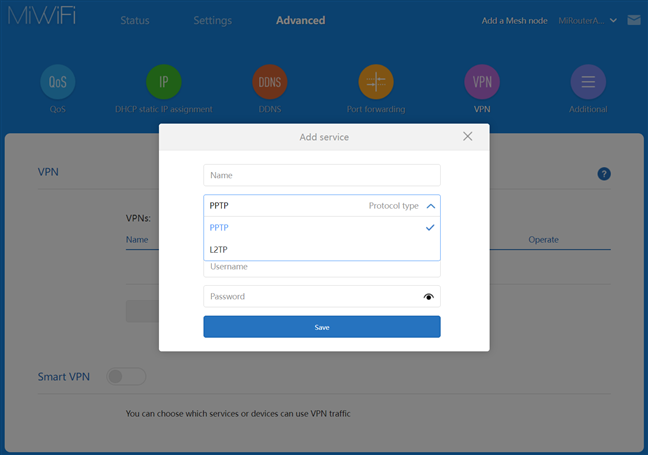
Xiaomi Mi Router AX1800 has few advanced features
What is your opinion about the Xiaomi Mi Router AX1800 router?
You know what we like about the dual-band Xiaomi Mi Router AX1800 and its most significant weaknesses. But, before closing this review, tell us what you think. Are you interested in purchasing this router? If you already own it, what has been your experience with it? Comment below, and let’s discuss.


 18.04.2022
18.04.2022 


