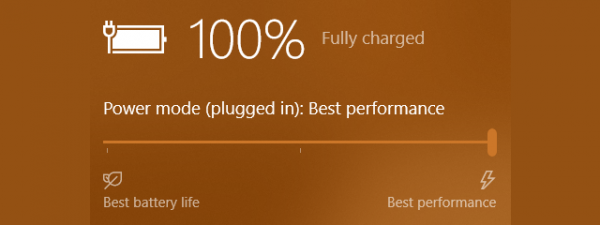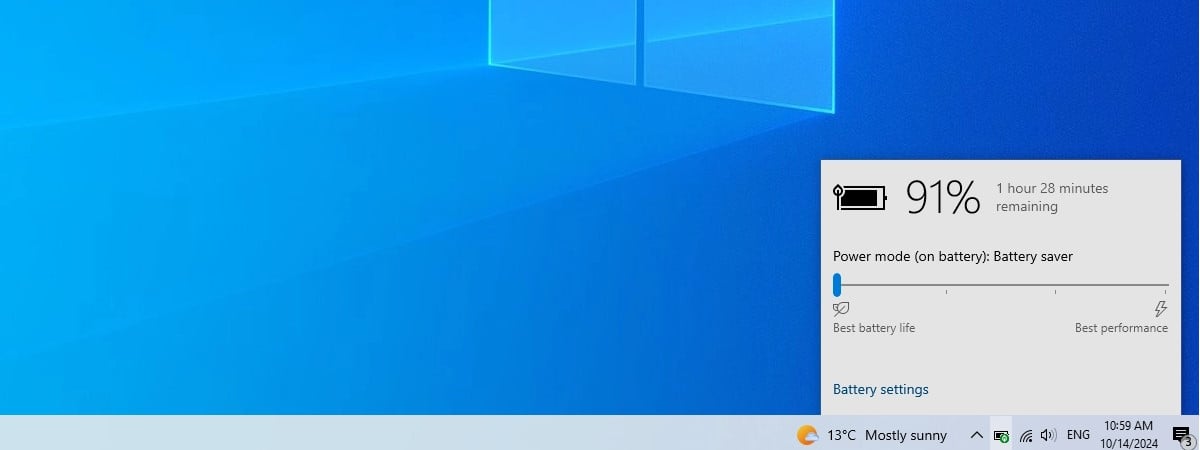
If you’re using a laptop, tablet, or 2-in-1 device, it’s likely you want to get the most out of its battery, but still have enough performance to handle whatever you’re doing. Fortunately, Windows 10 has a feature especially made for that, called the power slider. It’s found in the taskbar’s battery settings, and it lets you quickly switch between different power modes, depending on whether you want to save battery life or increase performance. In this tutorial, I’ll tell you more about the Windows 10 power slider and how to use it to get more battery or more performance from your device:
How to use the power slider in Windows 10
The power slider is available on laptops, tablets, and convertible devices that run on battery power in Windows 10 (since build 1709). To access the power slider, click or tap the battery icon in the system tray (lower-right corner of the screen).
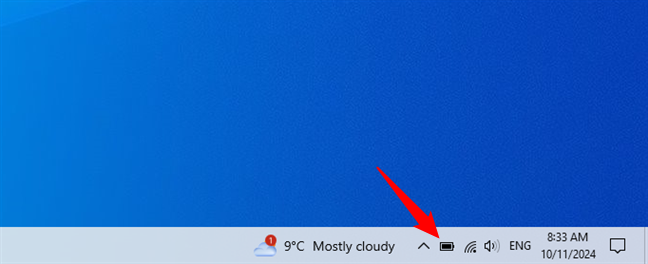
Click or tap the battery icon in the system tray
On battery power, the slider offers four positions: Best battery life (Battery saver), Better battery (or Recommended), Better performance, and Best performance. When your Windows 10 laptop is plugged into a power outlet, the slider is reduced to three positions: Better battery, Better performance, and Best performance. Simply move the slider to the desired level, depending on whether you prioritize battery life or system performance.
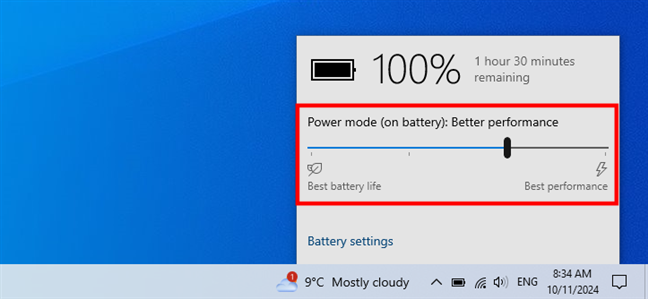
The power slider in Windows 10
You may ask: Why Better battery when connected to a power plug? Read the next chapter to see what each power mode does:
What power modes are available via the power slider?
The power slider has three or four positions, depending on whether you are connected to a power plug. Here’s what each position does:
- Battery saver: This mode provides maximum battery savings. It reduces power consumption by throttling certain features, limiting background activity, and lowering screen brightness. Useful when you need to conserve as much power as possible. You can learn more about this special mode, including how to configure it, in this guide: How to enable or turn off battery saver in Windows 10.
- Better battery: Offers longer battery life than the default settings but doesn't reduce performance significantly. This mode balances power savings and usability, and is often labeled Recommended.
- Better performance: The default setting for most users. It favors performance slightly over battery savings, allowing more background activity and ensuring apps run smoothly.
- Best performance: This mode prioritizes speed and power, sacrificing battery life. It’s ideal for tasks that require maximum performance, such as gaming or resource-intensive applications, but not suited for conserving battery power.
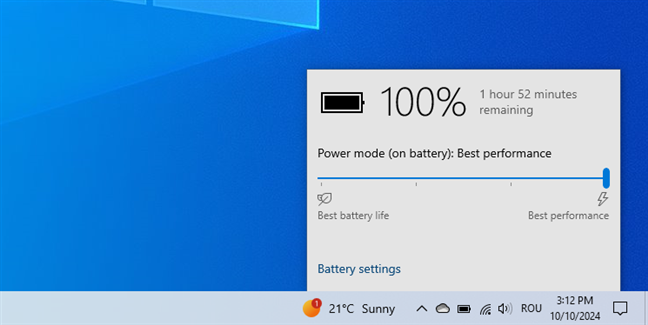
Setting the power mode to Best performance in Windows 10
Power slider vs. power plans
In older versions of Windows, battery life was managed exclusively through power plans like Balanced, Power saver, and High performance. Depending on the device, the power plans available for it can control settings like screen brightness, sleep timing, and how devices like hard drives or wireless cards operate on battery or while plugged in.
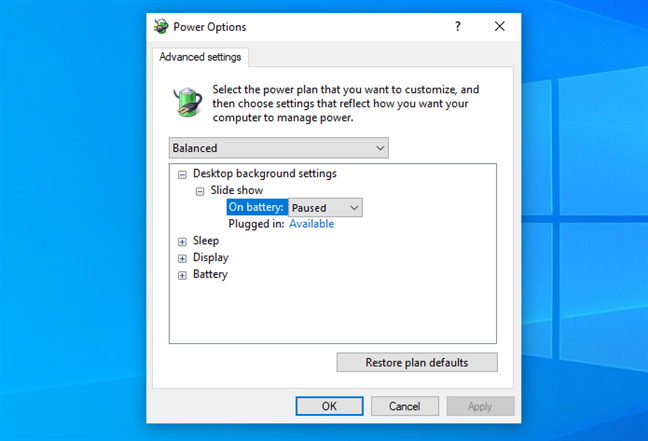
Settings available for a power plan in Windows 10
In Windows 10, the power slider simplifies the process by adjusting some settings dynamically, without requiring manual tweaks to a power plan. Power plans still exist, but are secondary to the power slider. The slider adds an extra layer of control, adjusting CPU performance, background app priorities, and screen brightness. In other words, the power slider dynamically applies changes based on user preferences, while power plans involve a more detailed, manual configuration.
Is the power slider missing? Why?
Not all Windows devices support the power slider. Here’s why:
- First of all, it was first introduced with Fall Creators Update (build 1709), which was released in October 2017. Older versions of Windows 10 don’t have this feature.
- Second of all, the power slider is available only for mobile Windows 10 devices that have a battery, such as laptops, tablets, and 2-in-1s. Desktop PCs and computers that are always plugged into a power source don’t use the power slider.
- Moreover, the power slider works only on systems with AMD and Intel processors with the Intel Speed Shift technology or similar technologies. For example, it works with Intel’s 6th generation Skylake processors that were released in August 2015. Newer AMD Ryzen and Intel processors all support this feature.
- And last but not least, another issue is that the power slider only works with the Balanced power plan or a custom plan that’s derived from it. If you switch to High Performance, Power Saver, or something else, the power slider is disabled. If you have multiple power plans available on your Windows 10 device, make sure you enable the Balanced one or the default provided by your system’s manufacturer. On some mobile systems, there is only one power plan available, created by the manufacturer of the device.
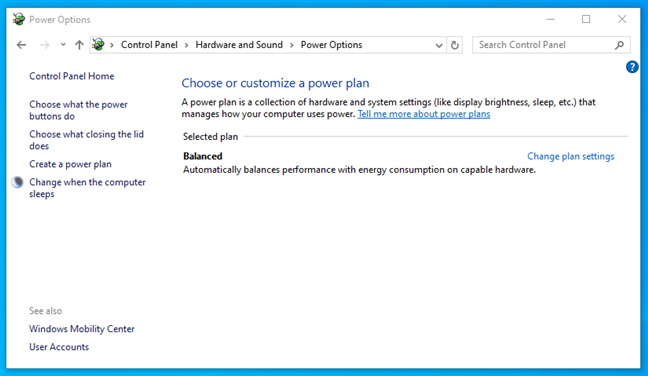
The power slider works only with the Balanced power plan
If you have met all these conditions and still don’t see the power slider, you may have stumbled upon a bug. In this case, all I can do is recommend that you reset Windows 10. It’s an option that requires you to reinstall your apps and reconfigure Windows 10, but it may be the only thing that can restore the power slider.
Do you use the power slider? How satisfied are you with this feature?
The Windows 10 power slider offers a simple yet efficient way of managing your device’s battery life and performance. By adjusting this slider, you can extend battery life when you’re on the go, or increase performance when running demanding applications or playing games. Try out the different power modes and see which one works best for you! Did you notice better battery life or improved performance when switching between the different power modes? Let me know in the comments section below.


 18.10.2024
18.10.2024