Both VPN (Virtual Private Networks) and proxy servers are designed to keep you anonymous on the internet. They can also help you access websites and services that are not available to everyone because of censorship or various restrictions. Proxies and VPNs each have their advantages and weaknesses, and some are better than others in certain situations. Do you know what to choose when? Should you use a proxy server, or do you need a VPN connection? When is it best to use one versus the other? Can you use a proxy and a VPN together? This guide explains everything you need to know about VPN vs. proxy servers:
What is a proxy server?
A proxy server is an intermediary waypoint between your computer or device and the internet. The proxy makes requests to websites, servers, and all kinds of internet services in your name.
For instance, if your web browser is configured to use a proxy server and you're trying to visit www.digitalcitizen.life, the request is not sent directly to our website. Instead, it goes to the proxy server. Once the proxy server receives your web browser's request, it forwards it to the server on which Digital Citizen is hosted. Then, our server responds and sends back the Digital Citizen homepage to the proxy server, which in turn sends it to your web browser.
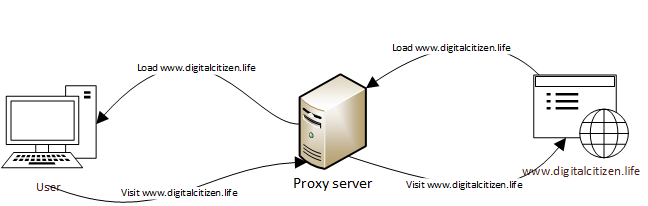
How a proxy server works
Because it's not your web browser that makes the direct request but the proxy server, our website does not see your computer or device as a visitor. Instead, it sees the proxy server as a visitor.
If you want more details about proxy servers and how they work, you should read this article: What is a proxy server, and what does it mean?. For even more information on how to set up a proxy on your device, check this list too:
- How to set up the proxy server settings in Windows 10
- How to set a proxy server in Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer, Microsoft Edge, and Opera
- How to set an Android proxy server for Wi-Fi: All you need to know
- How to set the use of a proxy server for Wi-Fi, on an iPhone or an iPad
Pros and cons of using proxy servers
Using a proxy server has the following advantages:
- You are hiding your IP address from basic checks. If you want to see a sample of what information about you goes out to the world during such a basic check, visit this webpage: Lookup IP Address Location.
- Using a proxy server means that you are also hiding your geographical location. The websites and services you access see the location of the proxy server that you are using instead.
- Depending on how they are configured, proxy servers can improve your security by blocking malicious websites that distribute malware because they can check for malicious content before it is sent to your computer.
- Proxy servers can be used to access geographically restricted internet services.
- There are many public free proxy servers available on the internet, and some provide reliable services.
On the other hand, there are also some negative aspects that you should consider:
- Proxy servers don't encrypt your internet traffic.
- Neither your IP address nor your real location is hidden from more advanced detection techniques. You can get an example of how your location can be detected with the help of your browser and its location services here: W3C Browser Geolocation.
- When using a proxy server, all your internet traffic goes through it. That means that a malicious proxy server can see and control everything you do on the internet, compromising your privacy and security.
- Proxy servers usually monitor and log your activity when using them, which can identify you. This can be harmful in certain situations.
- Although you're accessing a secured encrypted website or internet service, it can transfer unencrypted data to your computer if the proxy server was not configured correctly. In simple words, others can sniff your unencrypted information, which you probably don't want.
- There are many public free proxy servers available on the internet, and many of them are unreliable. Some of the free proxy servers are even downright malicious.
What is a VPN?
A Virtual Private Network or VPN is a secure network between your computer and a VPN server from the internet. All the network traffic through this connection is encrypted, so only your computer and the VPN server know what website or internet service you access and use.
For instance, if you use a VPN and try to visit www.digitalcitizen.life, the request is encrypted and sent to the VPN server. Once the VPN server receives your request, it decrypts it so that it knows what you want. In this case, it sends a load request to the server on which Digital Citizen is hosted. Our server responds by sending back the Digital Citizen homepage to the VPN server, which then encrypts it and sends it back to you.
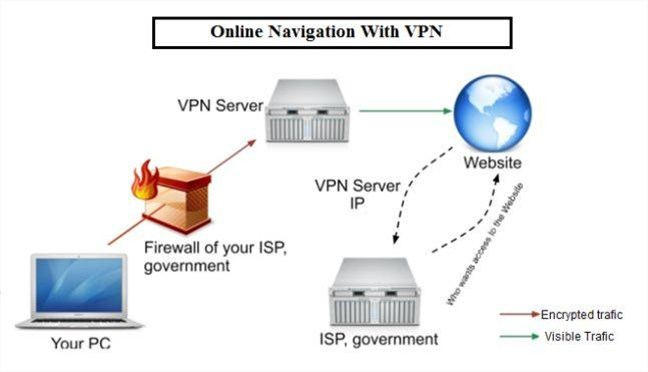
How a VPN works
Because every bit of data is encrypted, nobody can see what websites you visit and what internet services you use. That includes your government and your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
If you want more details about VPNs and how they work, read this article: What is a VPN? What does a VPN do?. For step-by-step guidance on how to set up and configure a VPN on your device, these tutorials should be of help:
- How to add and use a VPN in Windows 10 (all you need to know)
- How to create, configure, and use a VPN connection in Android
- How to create, configure, and use a VPN connection on an iPhone (or iPad)
Pros and cons of VPNs
Using VPN brings many benefits:
- All the network traffic between you and the VPN server is encrypted, so that makes it almost impossible for anyone to see what websites you visit or what services you use on the internet.
- VPNs hide your real IP address. Websites and internet services can only see the VPN server's IP address.
- VPNs hide your real geographical location. The internet thinks that your location is the location of the VPN server that you are using.
- Using a VPN server can help you bypass geographical restrictions. You can access content available only for some countries or regions if you connect to a VPN server from those regions.
- Your network traffic can't be sniffed because it's all encrypted.
- There are plenty of VPN providers that offer paid services, as well as free VPN servers.
Although VPNs have lots of advantages, there are also some not-so-positive features that you should consider:
- VPN servers must encrypt all the internet traffic that goes through them, which can take a toll on performance and speed.
- When you connect to a VPN server, every bit of data between you and the server is encrypted. However, that data is decrypted on the VPN server, so it knows what you do on the internet. VPN providers mustn't keep logs about your activity. Otherwise, the VPN provider knows how you are using its service. Those logs can also be used by other organizations that get authorized or unauthorized access to it.
- Trustworthy VPN services tend to have higher costs than what you'd pay for a good proxy. All that encryption means that VPN servers must have powerful hardware to keep up with the demand.
- Many of the free VPNs aren't trustworthy and, in some cases, can even be dangerous.
At the end of this section, we’d like to point out a few of the VPNs we tested and liked, so that you can make an informed choice: CyberGhost, NordVPN, F-Secure Freedome VPN.
VPN or Proxy? Comparing the advantages and disadvantages of proxies vs. VPNs
To make it easier for you to see all the advantages and disadvantages of using a proxy server versus using a VPN service, we created this comparison table:
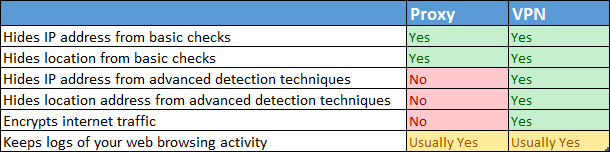
Proxy vs. VPN comparison
Also, to sum everything up, the main things you should keep in mind are:
- Unlike proxy servers, VPNs encrypt the data you send and receive over the internet.
- Good VPN services tend to protect your privacy and don't keep logs about your online activity.
- Although, in general, VPNs are better than proxy servers, they also tend to cost you more money.
- If you only want to hide your IP address, a proxy does the job. If you also want to hide the data you transmit, only a VPN can help you.
- Neither using a VPN nor a proxy server can offer you complete security in our interconnected world. It would be best to also install and use a good security solution to protect yourself from ransomware attacks, keyloggers, viruses, and other similar threats.
When to use a proxy and when to use a VPN?
We consider VPNs better than proxies in almost all respects. VPNs are better at providing you with anonymity, and they are certainly better at providing you with security. Everything you do on the internet while using a VPN service is encrypted, and nobody can monitor or track your activities. The only major downside of VPNs is that they tend to cost a lot more than proxies. If all you want is to hide your IP address or physical location from a website or internet service that only does elementary checks, then maybe a proxy server is good enough for you. If you want anonymity, security, and confidentiality, then subscribing to a VPN service is what you need. However, double-check that it doesn't store logs of your activity and, if they are stored, they are not shared with third parties.
Finally, if you're wondering whether you can use a proxy and a VPN together, at the same time, the answer is yes. However, it's not something we recommend because the VPN already does the proxy's job, while also encrypting your traffic. Furthermore, even if you might be tempted to think that a proxy server is faster than a VPN, if you use both, the internet speed you get in the end is actually the one of the slower service: either that of your proxy or that of your VPN.
VPN vs. proxy: Which one is right for you?
Both proxy servers and VPNs are useful tools, no question about it. Now that you know everything there is about using proxy vs. VPN, we want to know what do you prefer? Is a proxy enough for your needs? Are you willing to pay for your online security or is a free service enough for you? Let us know in the comments.


 03.11.2020
03.11.2020