You may be familiar with the term Safe Mode in Windows, but do you know what it means and what it does? Do you want to learn more about it and how it differs from regular Windows? What about the differences between the three Safe Modes available on Windows operating systems? To get answers to all these questions, read this article:
What is Safe Mode? What does Safe Mode do?
Let’s start with the basics: What’s Safe Mode? Well, Safe Mode is a special Windows mode that helps you troubleshoot your computer or device. It only runs the most essential services and processes, skipping anything unnecessary for Windows to start.
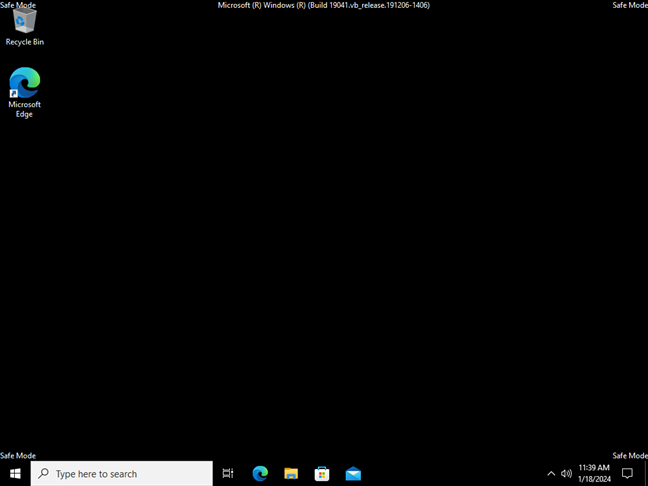
What Safe Mode looks like in Windows 10
The Safe Mode(s) in Windows 11 and Windows 10 are essentially the same. At least from what I’ve seen, both operating systems offer the same experience and behave identically when you use their Safe Modes.
Why is Safe Mode important?
Safe Mode is a useful feature of the Windows operating systems, allowing you to troubleshoot your computer or device more easily. Because Windows loads only the most critical drivers and software when you boot your computer in Safe Mode, it avoids using any hardware components or apps that could cause problems or interfere with the system.
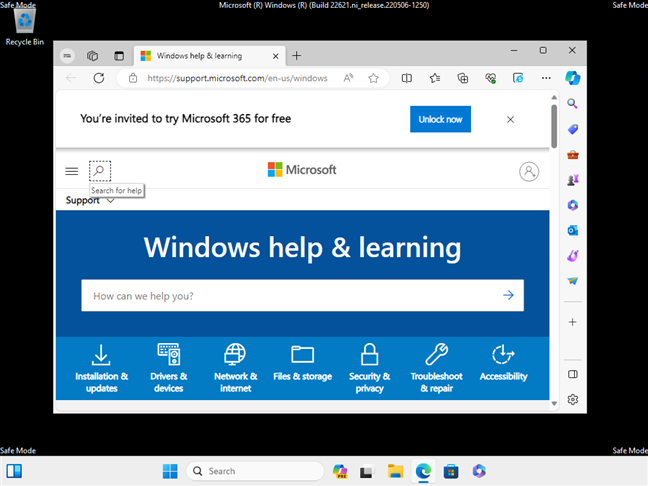
Safe Mode with Networking in Windows 11
Therefore, it significantly reduces the chance of encountering errors or conflicts caused by faulty or incompatible components. For example, since it only uses a basic set of video drivers that are compatible with most devices, not the full-fledged drivers provided by your GPU manufacturer, Safe Mode can help you identify and fix issues with your graphics card.
What can you do in Safe Mode on a computer?
As we know now, Safe Mode helps us troubleshoot issues with our Windows computers and devices. But how exactly? Here are some things you can do in Safe Mode on a Windows PC:
- Use the built-in troubleshooting tools to diagnose and fix problems with network, sound, graphics, and other components.
- Run Windows Terminal, Command Prompt, or PowerShell to execute advanced commands that can repair disk errors, network problems, boot issues, and more.
- Download (if you use Safe Mode with Networking) and run programs that can help you resolve the issues with your PC.
- Download (if you use Safe Mode with Networking) and install or uninstall drivers for some hardware devices with bugs or compatibility issues.
- Scan your PC for malware or other security threats using antivirus software.
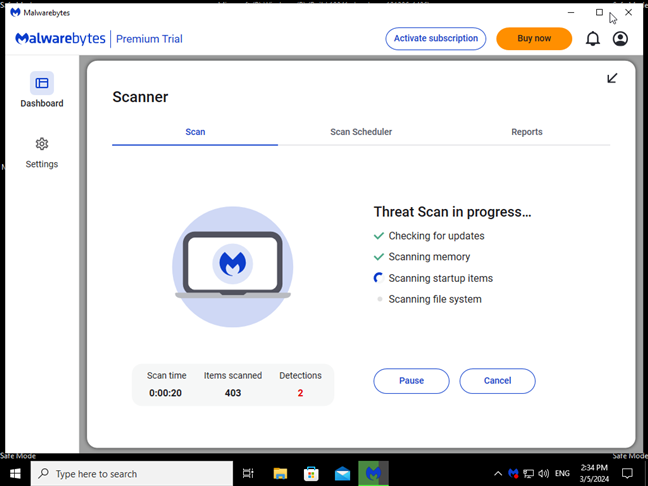
Using Safe Mode to scan and clean an infected computer
On the other hand, because this is a diagnostic mode that only loads the essential drivers and services for Windows to run, some features and apps that depend on your hardware are unavailable in Safe Mode. For instance, you can’t play games in Windows Safe Mode, as they require the full functionality of your graphics card and other components. Safe Mode is designed to help you troubleshoot problems, not to offer a regular desktop experience. 🙂
Why are there multiple Safe Modes in Windows? What’s different?
Windows offers three variations of Safe Mode: regular Safe Mode, Safe Mode with Networking, and Safe Mode with Command Prompt. While all modes are designed to help troubleshoot and fix common issues with the operating system, they are different from each other in terms of functionality. Here are the key differences between them:
What is regular Safe Mode in Windows?
The “normal” Safe Mode starts Windows 11 and Windows 10 with a basic graphical interface and only the essential drivers, services, and processes so that you can easily isolate and fix any problems that might be caused by incompatible or faulty software or hardware.
Safe Mode in Windows 10
If you need to enter the normal Safe Mode on your laptop, PC, or hybrid devices, follow these guides:
What is Safe Mode with Networking?
This mode enables everything in the “regular” Safe Mode and adds networking capabilities. It allows you to access other computers on your local network and gives you access to the internet, too, but only through a cable connection, not Wi-Fi. You can use this mode to visit websites and search for documentation or troubleshooting guides. This is also the mode you should enable if you need to download and use special tools for identifying and resolving issues on your Windows computer.
Safe Mode with Networking in Windows 10
If this is the Safe Mode you need, here’s how to boot into it:
- How to start Windows 10 in Safe Mode with Networking
- How to start Windows 11 in Safe Mode with Networking
What is Safe Mode with Command Prompt?
This last mode is a variation of Safe Mode that only loads the Command Prompt instead of the desktop. You can use it to run commands when the Windows graphical user interface causes problems in the standard Safe Mode. Safe Mode with Command Prompt lets you access and fix Windows even if the desktop, File Explorer, or other visual tools fail to load.
Safe Mode with Command Prompt in Windows 10
Here’s how to start Windows 10 in Safe Mode with Command Prompt and boot Windows 11 in Safe Mode with Command Prompt.
TIP: Once you’ve finished troubleshooting your PC, you can get out of Safe Mode and try booting Windows normally. When you get to that, here’s how to turn off Safe Mode in Windows 10 and Windows 11.
What do you use Safe Mode for?
Safe Mode is one of the most important features of Windows, as it can help you troubleshoot various issues with your computer or device. It’s the go-to place I turn to when my Windows desktop PCs and laptops are no longer working properly and I need to find out what’s wrong. Before you leave, I’d like to know more about your experience with Safe Mode and how it helped you solve your PC problems, so please share with us if you can.


 11.03.2024
11.03.2024