If you ever used a Windows PC or a storage device like a USB memory stick or an SD card, it is almost impossible that you have not heard about FAT32. It is one of the most popular file systems ever used on storage devices of all kinds. If you want to learn more about its history, its purpose and uses, read on. In this article, we are talking about FAT32:
What is FAT32?
FAT32 is a file system used for storage devices, and file systems are ways of organizing storage on devices such as hard drives, SSDs, memory sticks, microSD cards, and so on. FAT32 is also an acronym for File Allocation Table 32, and the 32 part of its name comes from the fact that FAT32 uses 32 bits of data for identifying data clusters on the storage device.
When was FAT32 invented and by who?
FAT32 is a file system that was first introduced to the world in 1996, by Microsoft, which used it in MS-DOS 7.1 and Windows 95 OSR2. FAT32 is the next in line after FAT16 and FAT. The original FAT file system was initially designed and used way back in 1977. Its purpose was to be used on floppy disks, but with the advance of computing technology, it was soon the default choice for formatting hard drives too.
FAT and its derivatives, including FAT32, were the most popular file systems used by DOS (Disk Operating System) and Windows computers since the 1980s and up until the year 2000. FAT32 began to lose importance in 2001, when Windows XP was launched, which used NTFS rather than FAT32 by default.
FAT32 remains one of the most popular file systems in the world today, as it is still used on a large scale for formatting all kinds of storage devices.
The pros of using FAT32
FAT32 had some good things about it, otherwise it would not have managed to live for such a long time. However, the only important advantages of using FAT32 today are:
- It is compatible with a huge variety of devices: smartphones, tablets, computers, digital cameras, gaming consoles, surveillance cameras and so on.
- It is also cross-compatible with almost all operating systems that were launched since 1995 and up until now. FAT32 works with Windows 95 OSR2, Windows 98, XP, Vista, Windows 7, 8, and 10. MacOS and Linux also support it.
The cons of using FAT32
There are some serious disadvantages to using FAT32 on your drives:
-
FAT32 can only work with files that are less than 4 GB in size.
-
FAT32 only works with partitions with a maximum capacity of 8 TB.
- If you have a drive that is formatted in FAT32, you do not get any data protection in case of power loss.
- The FAT32 file system does not include any built-in file compression features.
-
FAT32 was not designed to be secure and does not include any built-in encryption features. If you want to encrypt files on a FAT32 formatted drive, you must use third-party tools for that.
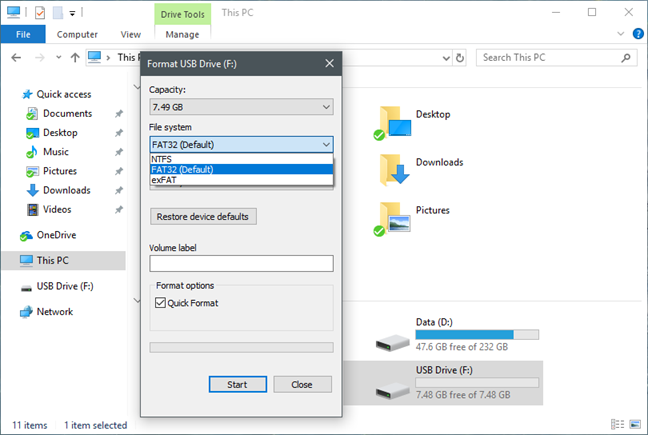
Is FAT32 faster or slower than NTFS?
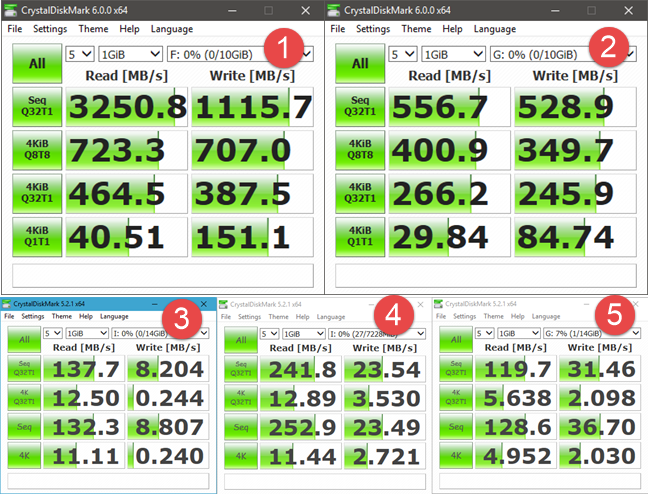
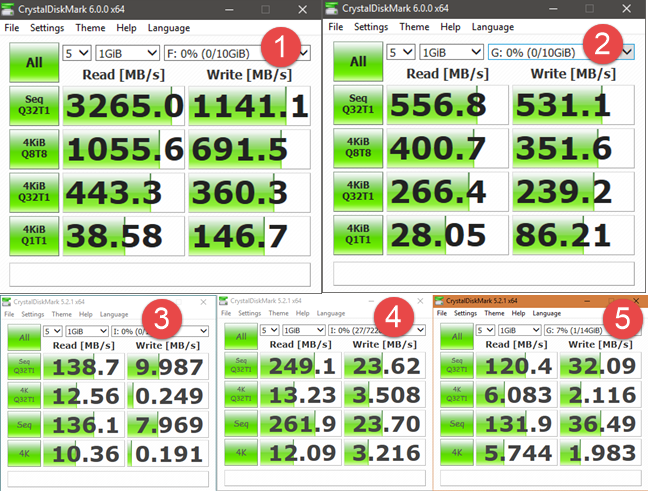
FAT32 is also slightly slower than NTFS, which is the most used file system on Windows devices. To compare the actual decrease in speed, we used a few storage devices and measured their read/write speed using CrystalDiskMark. The storage devices that we used are:
- the 256GB Samsung NVMe M.2 PCI Express X4 SSD found in our Lenovo Legion Y520 laptop (represented by number 1),
- a 250GB SATA III Samsung 750 EVO SSD (represented by number 2),
- a Kingston DataTraveler microDuo 3C (represented by number 3),
- an IronKey D300 (represented by number 4), and
- a SanDisk Ultra Fit (represented by number 5).
In the screenshot below, you can see the speeds that we measured when we formatted these storage drives using FAT32.
Here are the speeds we got when we formatted the same drives using NTFS:
From looking at these results, you can see that both solid state drives (represented by the numbers 1 and 2) were slower at reading data from a FAT32 file system. The results were similar when writing data. We can also see the same trend with the IronKey D300 (represented by number 4) and with the SanDisk Ultra Fit (represented by number 5), which were also slower at reading data when using FAT32 instead of NTFS.
We conclude that using FAT32 is best when you want cross-compatibility between various devices and operating systems. However, if you want speed, FAT32 is not the best choice you could make. For that, NTFS is better, especially on solid state drives, where the reading speeds are quite a bit higher compared to the old FAT32 file system.
Do you use FAT32?
It is highly unlikely that you did not stumble on a storage device formatted using FAT32 at least once in your life. The reason for its popularity and long life is this cross-compatibility between devices from different manufacturers and between various operating system. To be honest, this is the sole reason why you might still want to use FAT32. Before closing this guide, we are curious to know whether you still use it, and on what kind of storage devices. Share your thoughts and experience with FAT32, in a comment below.


 28.03.2018
28.03.2018