Have you encountered the terms disk image or ISO image? You may have heard them from a tech-savvy friend who has a huge library of disks (CDs, DVDs, Blu-Ray disks), but he or she doesn’t appear to use any of them, at least not regularly. Well, that friend of yours most likely has created disk images of all the optical disks he or she uses more often. What are disk images, and why would someone create or use disc images? Read this guide, and by the end, you will have the answers to these questions and more:
What is a disk image?
A disk image is a file that stores an entire disk’s content and structure. That disk may be an optical disk like a CD, DVD, Blu-Ray disk, hard disk or solid-state drive, USB flash drive, tape drive, and so on. A disk image is a file that’s the exact copy of a disk volume or an entire physical disk drive. This copy retains all the properties of its source: files, folders, properties, and the disk’s name.

A disk image is an exact replica of the original disk
How is a disc image file useful?
Disk images are a handy way of storing backup copies of your disks. For instance, you might still have some Audio CDs you play regularly. You probably don’t want them to wear out fast because you use them often. In that case, a good way to listen to them but keep them in a pristine condition - because you will not use them - is to create disk images for them. The disk images can be stored on your computer, and you can simply mount them when you want to listen to your music. Obviously, you can rip their contents into another format, but that’s another story.
A Windows 11 install media stored as an ISO disk image
The usefulness of creating disk images for your Audio CDs is just an example, but there are more situations where disk images prove their worth. For instance, some software vendors choose to deliver their programs as disk images you can download from the internet. A very good example is operating systems, which are often delivered online as ISO disk image files. That’s because disk images are replicas of physical DVD disks, and installing an operating system usually means having it on a bootable disk. If you get the operating system as a disk image, which is a single file that you can download from the internet, you can then burn it on a CD or DVD, and finally, you can use it to boot and install the operating system.
What are the main benefits of disk imaging?
To sum it a bit up, here are some of the most prominent benefits of using disk images:
- Disk images are exact replicas of disk drives or disk volumes, so they faithfully preserve all details related not only to content but also to the original files and folders structure;
- A disk image of an optical disk can be very useful when you need to create multiple copies of that disk;
- A disk image of a hard drive that contains a Windows operating system can be used to clone Windows on another drive extremely fast (though you’ll need specialized software for that);
- A disk image of a hard disk or an optical disk has the big advantage of portability. Being a single file, it is easy to send it online to others or store it on an external hard disk drive, for instance.

Disk imaging can be quite useful in many situations
Which are the most common file formats for disk image files?
As we know by now, a disk image is a file stored on your disk. Like any file, it must bear a name and an extension. In other words, every file has a file format. The most common disk image file formats today are:
- ISO - by far, the most popular disk image file format currently in use. The name ISO comes from the file system used by optical media (usually ISO 9660). ISO files are automatically identified by modern operating systems and can be mounted without requiring third-party software. Check the next sections of this article for details on that.
- IMG - raw disk image files of magnetic disks or optical discs; these files can be opened only by applications that can detect their file systems.
- BIN & CUE (Cue Sheet File) - are CD or DVD disk images split into two different files. One of them is a .BIN file, which is a binary file that’s an exact copy of the disk. The complementary .CUE file contains the details on how the data is structured on the original disk.
- MDF & MDS (Media disk Image File & Media Descriptor File) - the CD or DVD image is stored inside the .MDF file, while the header and track information are stored in the MDS file.
- NRG (Nero CD/DVD Image File) - are CD or DVD disk images created with the Nero disc authoring software.
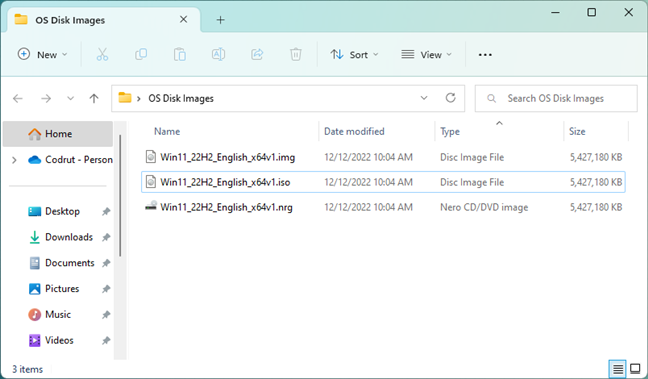
Different types of disk image files
If you’d like to know more about all the disk image file types known to man :), check this web page: Disk Image Files.
How do you create disk images in Windows?
To create a disk image, you need to use a software application that’s able to do this. Unfortunately, Windows doesn’t know how to create disk images, and the only way to do that is by using a third-party program. There are many such programs available on the internet, and most focus on either creating disk images of CDs, DVDs, or Blu-ray disks or on creating disk images of hard drives of all kinds.
We’ve covered some scenarios related to creating disk images for optical disks in these two tutorials: How to copy optical discs (CD, DVD, or Blu-Ray) in Windows and How to make a backup copy of a protected disc (DVD or Blu-Ray).
How do you mount a disk image in Windows?
Windows 10 and Windows 11 know by default how to work with the most common file format for disk images: ISO images. If you want to use a disk image as a virtual CD/DVD or Blu-ray disk in Windows, and if it is an ISO image, you can simply mount it by double clicking on it (or right-clicking and selecting Mount). When a disk image is mounted, it looks and works the same as if it were a physical disk loaded into an optical media unit. To find out how we recommend you follow the steps described in this guide: How to open (mount) or eject (unmount) ISO files in Windows.
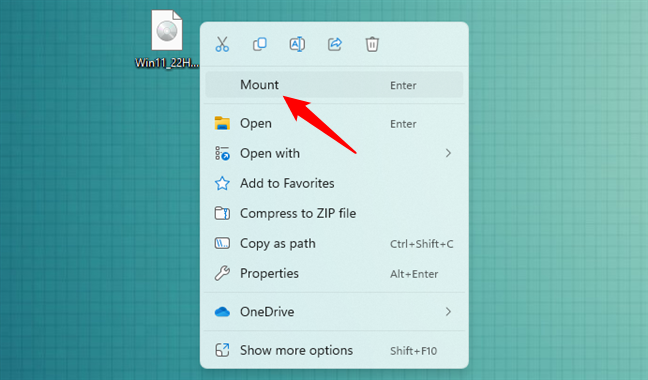
Mounting an ISO disk image in Windows 11
If you need to work with disk images that use other, more exotic file formats, then you’ll have to install a third-party tool like the ones we suggested in this roundup: The best free programs to mount disc images in Windows. We recommend WinCDEmu, a tiny (2MB) open-source emulator that allows one-click mounting of all the common disk images: ISO, CUE, NRG, MDS/MDF, CCD, IMG. It works in every Windows version from Windows XP onwards (including Windows 10 and Windows 11), it’s free, and it supports an unlimited number of virtual drives.
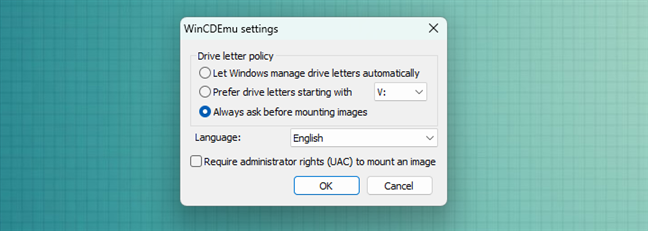
WinCDEmu: Free open-source optical media emulator
How do you burn ISO disk images in Windows?
If you have an ISO or an IMG disk image and you want to burn it to a physical CD/DVD or Blu-ray optical disk, then this guide will provide you with the steps on how to do that in Windows without using any third-party tools: Burn disc images with Windows Disc Image Burner (ISO to Blu-Ray, DVD).
Are you using disk imaging?
Now you know what disk images are, why they are useful, how to mount them in Windows and how to create your own disk images. Hopefully, we have managed to answer all your questions on this subject. If we didn’t, let us know in the comments section below. We will do our best to help.


 22.12.2022
22.12.2022