The Windows Terminal is the latest effort from Microsoft in turning the use of command-line tools and shells into a pleasant experience, similar to the one offered by Linux and other operating systems. However, if you are interested in learning how it works and how to use it, you first need to know how to open it. To help you out, here’s a long list of all the ways in which you can start the Windows Terminal, with and without administrator privileges:
NOTE: If you use Windows 10, make sure that you have installed the Windows Terminal first. Here’s how to get the Windows Terminal app. If you use Windows 11, there’s nothing you need to do before using the Windows Terminal.
1. Open the Windows Terminal using search
One of the fastest ways to start the Windows Terminal is to use search. In Windows 11, click the Search icon and then type “terminal” or “windows terminal.” Press Enter on your keyboard when you see the Windows Terminal search result or click or tap the search result itself or the Open option on the right. If you need to run this app with administrator permissions, press the arrow pointing downwards on the right of the search result, and then choose “Run as administrator.”
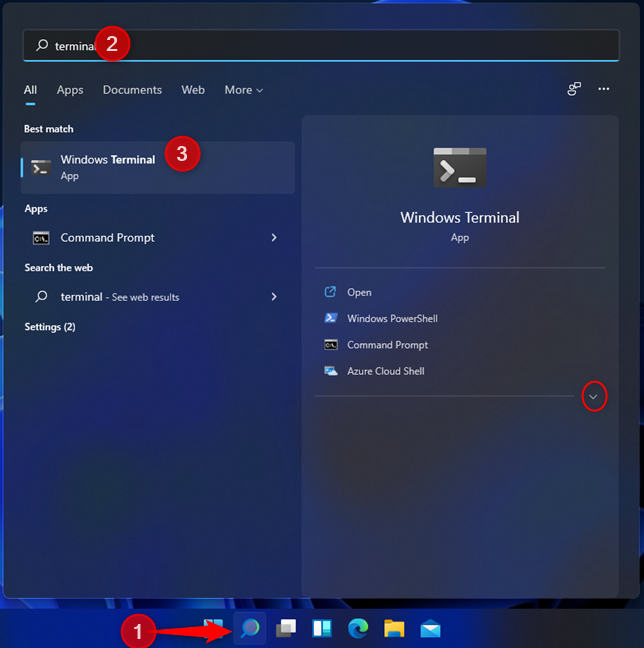
Search for terminal in Windows 11
In Windows 10, click inside the search box from the taskbar and type “terminal” or “windows terminal.” Then, click or tap the Windows Terminal search result. You can also click or tap the Open option on the right. To see the “Run as administrator” option, first press on the arrow pointing downwards.
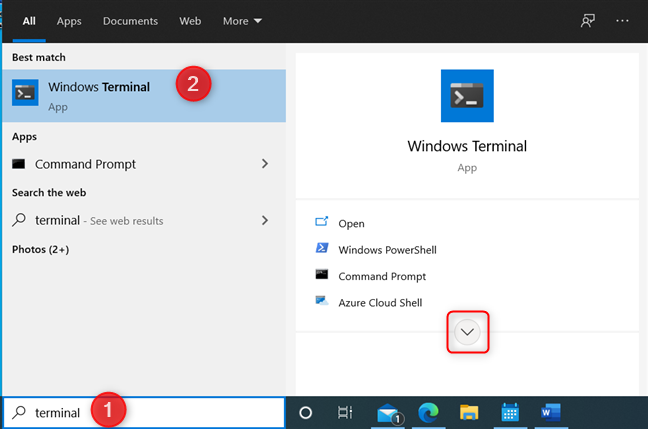
Search for terminal in Windows 10
2. Use the Run window to open the Windows Terminal
Another fast method is to open the Run window by pressing the Windows + R keys on your keyboard. Then, type wt and press Enter or click OK.
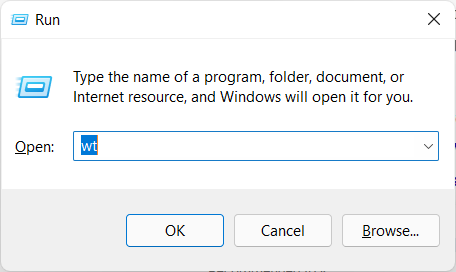
Run the command wt
3. Use the WinX menu to start the Windows Terminal (Windows 11 only)
The Windows Terminal is included by default in Windows 11 and promoted by Microsoft as the main command-line app. The company wants people to get used to it and use it instead of the traditional Command Prompt and PowerShell. Therefore, the Windows Terminal is included in the WinX menu. To access it, right-click (or press and hold) the Windows logo on the taskbar, or press the Windows + X keys simultaneously on the keyboard. In the WinX menu, notice the Windows Terminal and Windows Terminal (Admin) entries. The second one starts the app with administrator permissions. Before you can run it, you also see a UAC prompt where you should press Yes, so that the Windows Terminal is allowed to run.
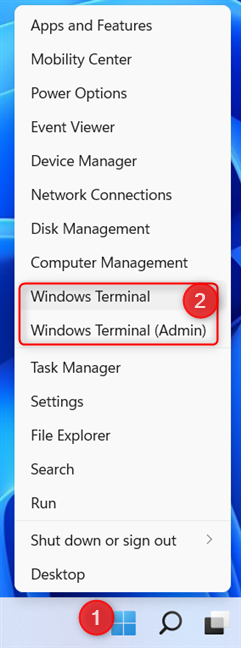
The WinX menu can be used to open the Windows Terminal
NOTE: This method does not work in Windows 10.
4. Run the Windows Terminal from the Start Menu
This method is a bit slower than the previous ones. If you use Windows 11, click or tap on Start (the Windows logo) and then on All apps.
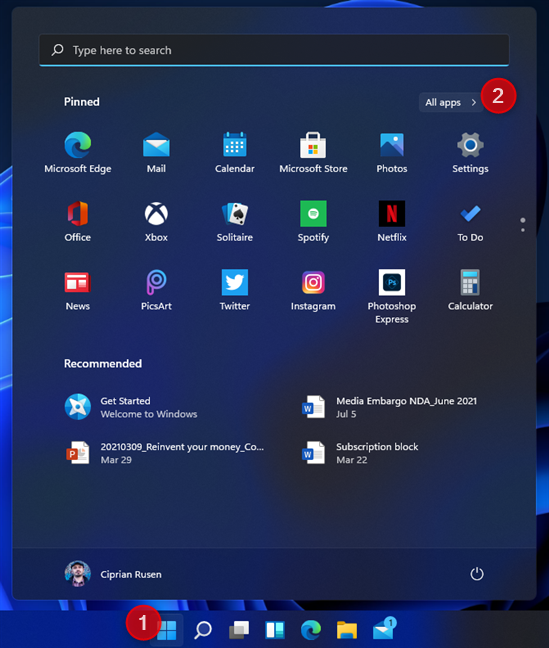
Open the Start Menu and go to All apps
Scroll down the list of apps to the letter W and press the Windows Terminal shortcut. To run the app with administrator permissions, right-click (or press and hold) on its shortcut and select More, followed by “Run as administrator.” Don’t forget to press Yes when you see the UAC prompt.
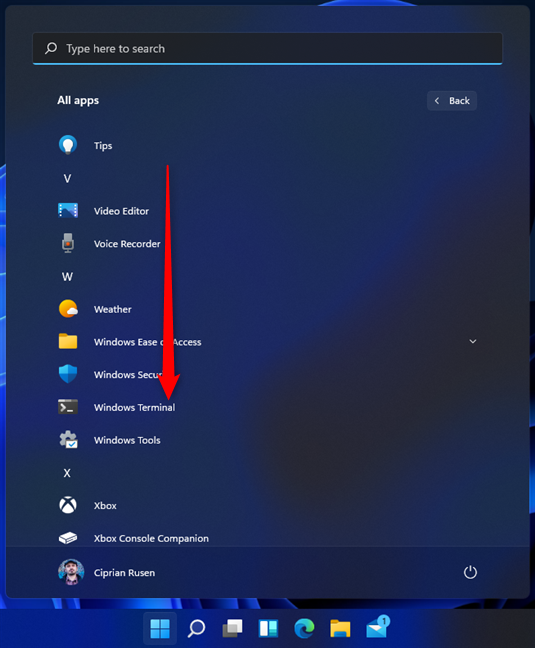
Scroll down to the Windows Terminal shortcut
In Windows 10, the steps involved are slightly fewer: click or tap Start, and then scroll down the list of apps to Windows Terminal. Press on the shortcut to open the app.
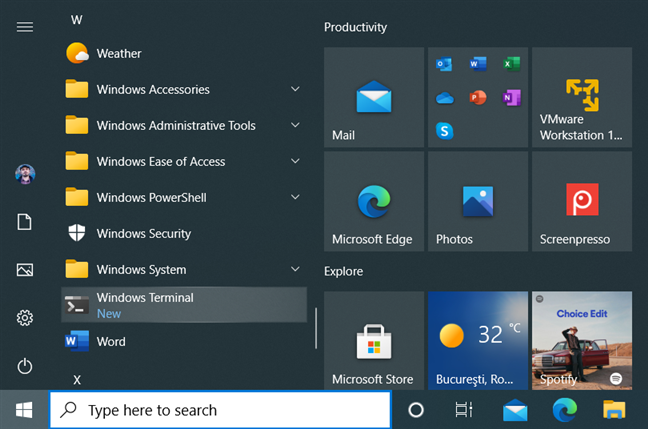
The Windows Terminal shortcut in the Windows 10 Start Menu
To start it with administrator permissions, right-click or press and hold the Windows Terminal shortcut, and then choose “More -> Run as administrator.”
5. Open the Windows Terminal by creating a shortcut
You can also create a shortcut for the Windows Terminal to place on the desktop or someplace else. To do that, right-click (or press and hold) on the empty space on the desktop and choose “New item -> Shortcut.”
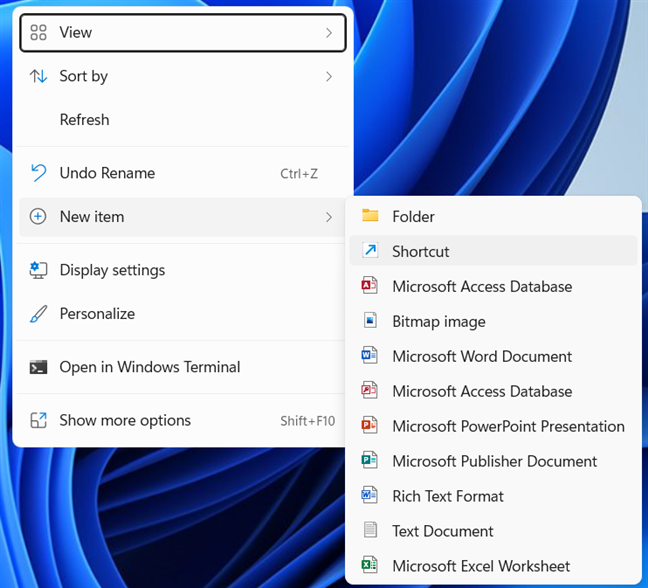
Create a new shortcut
In the Create Shortcut wizard, type wt as the location and follow the rest of the wizard. Give the shortcut a name and keep it on the desktop or move it where you want.
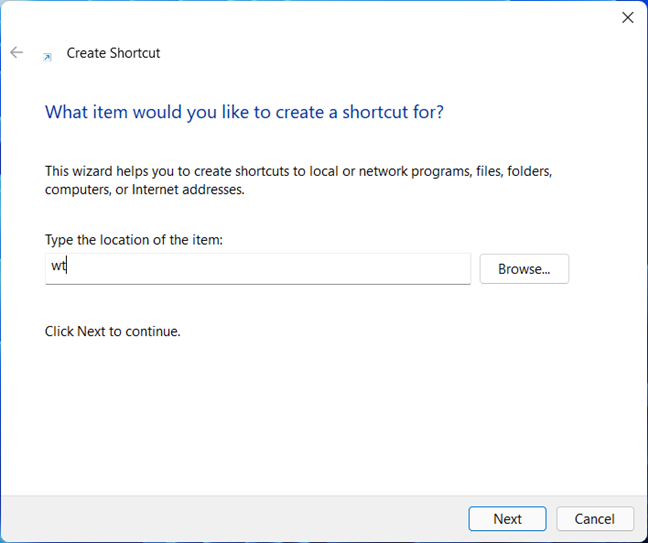
Write wt as the target of the shortcut
If you need help shortcuts, read our guide on creating shortcuts for apps, files, folders, and web pages in Windows.
6. Start the Windows Terminal from Command Prompt or PowerShell
If you find yourself inside the Command Prompt (CMD) or PowerShell, you can run the Windows Terminal from both. All you have to do is enter the command wt and press Enter.
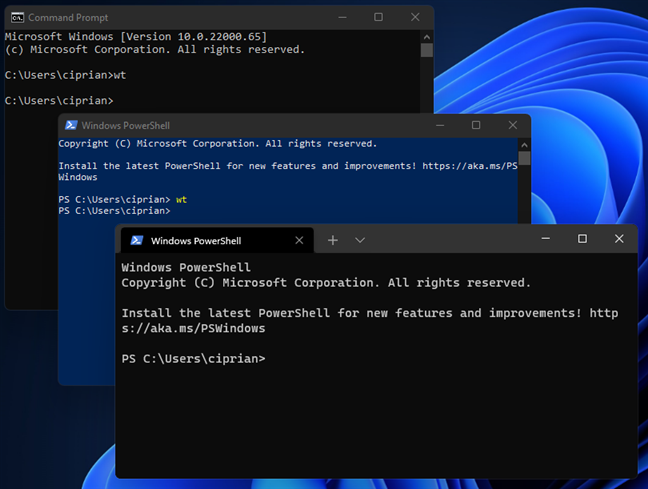
The Windows Terminal can be opened from CMD and PowerShell
The Windows Terminal is immediately opened as a separate window. Also, if CMD or PowerShell were opened as administrator, the Windows Terminal inherits the same administrator permissions.
7. How to open the Windows Terminal from File Explorer's address bar
If you are browsing the files and folders on your computer using File Explorer, you can start Windows Terminal from there too. In the address bar on the top side of File Explorer, type wt and press Enter on your keyboard.
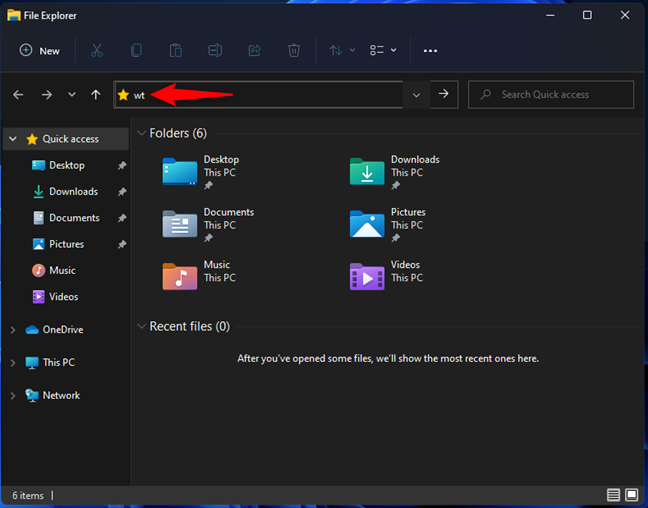
Run the Windows Terminal from File Explorer
The Windows Terminal opens immediately. Unfortunately, you cannot open the Windows Terminal as an administrator using this method.
8. Start the Windows Terminal using Cortana
If you have a microphone installed on your Windows 11 computer or device, you can also tell Cortana what you want to do. First, start Cortana by pressing on her shortcut from the Start Menu or with the Windows + C keyboard shortcut. Then, ask Cortana to "start the terminal" or "open the windows terminal."
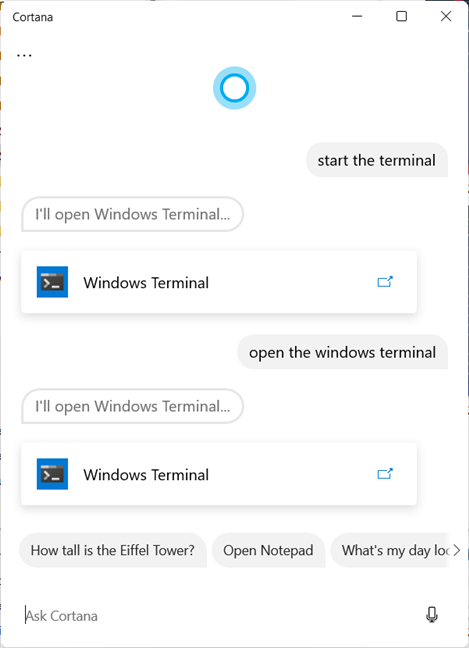
Cortana can start the Windows Terminal for you
This method works both in Windows 11 and Windows 10. However, you can’t use it to open the Windows Terminal as administrator.
9. Open the Windows Terminal from the Task Manager
Few people know that you can use the Task Manager to start apps too, not just terminate their processes. You can use it to open the Windows Terminal as well. To do that, start the Task Manager (press Ctrl + Shift + Esc). If you get the compact view of the Task Manager, first press More details. Open the File menu, select "Run new task," and then type wt in the "Create new task" window. Press Enter on your keyboard or press the OK button. If you want to run the Windows Terminal as an administrator, don’t forget to check the "Create this task with administrative privileges" setting before you do that.
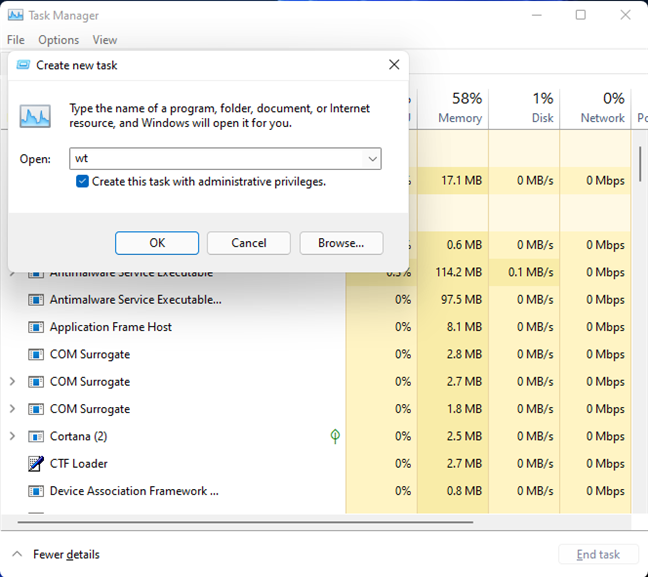
The Windows Terminal can be opened from the Task Manager
Which is your favorite method for opening the Windows Terminal?
These are all the ways we know for starting the Windows Terminal in Windows 10 and Windows 11. If you know other methods, let us know in a comment. Also, don’t hesitate to tell us which method you prefer from our list and why. We’re curious to know which methods our readers like the most.


 19.07.2021
19.07.2021