When you have problems with your network and/or internet connection, don't hesitate to use the troubleshooting wizards that are bundled with Windows. They are easy to use and they can help you identify what's wrong and how to fix your problems. In most cases, they will get the job done and help you more than expected. In this tutorial, we will show you how to start the network and internet troubleshooting wizards that Windows has to offer and how to work with them in order to fix your networking problems.
NOTE: This guide applies to Windows 10, Windows 7 and Windows 8.1 users.
How to find the network and internet troubleshooting wizards in the Control Panel
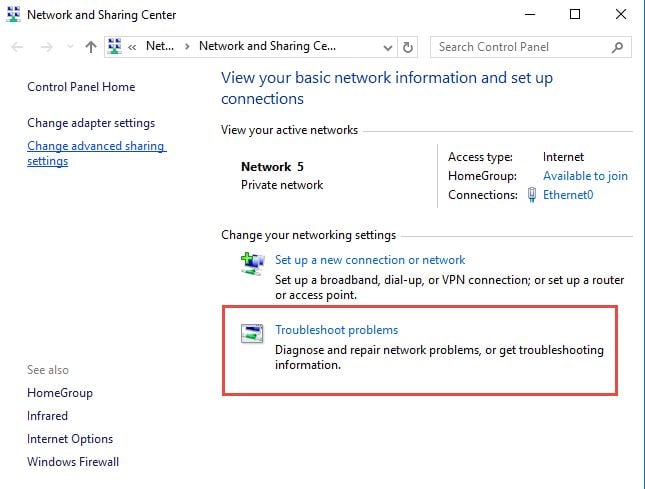
One of the easiest ways to access the network and Internet troubleshooting wizards is to open the Network and Sharing Center by going to "Control Panel -> Network and Internet -> Network and Sharing Center" . Then, click or tap the "Troubleshoot problems" link on the bottom of the window. While the Network and Sharing Center window looks a bit different, depending on the version of Windows that you are using, the "Troubleshoot problems" link is always on the bottom of the window.
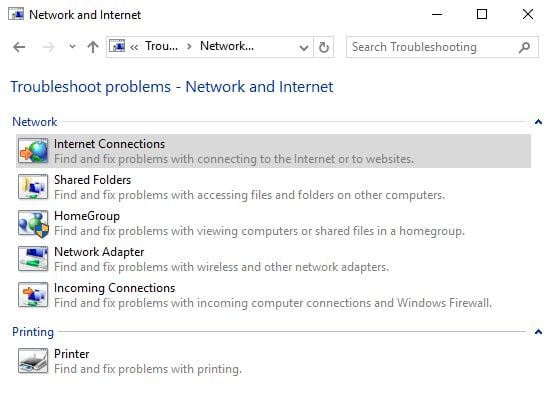
This opens the list of network and internet troubleshooting wizards that are available in Windows: Internet Connections, Shared Folders, HomeGroup, Network Adapter and Incoming Connections . If you have a printer installed on your Windows computer, you will also see a Printer troubleshooting wizard.
How to use search to start the troubleshooting wizards
As always, you can also use search to launch the troubleshooting wizards.
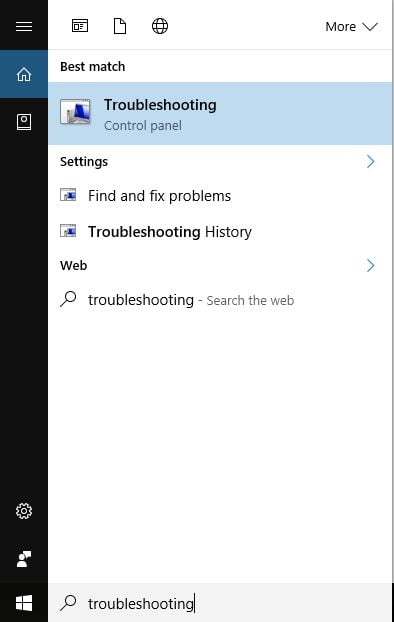
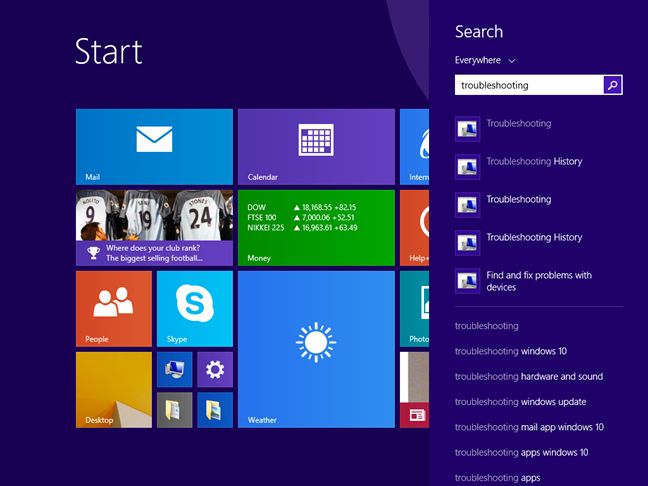
In Windows 10, in Cortana's search box on the taskbar, type the word troubleshooting and click or tap the search result with the same name.
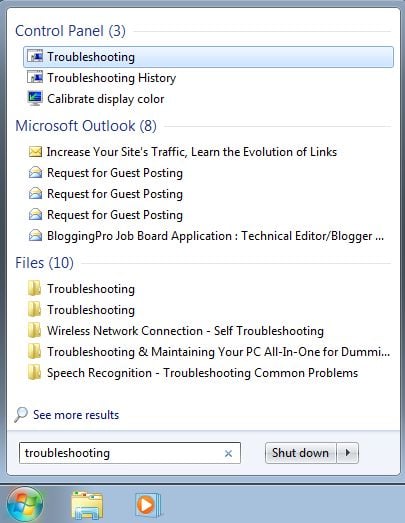
In Windows 7, type the word troubleshooting in the Start Menu search box. Then, click the Troubleshooting search result.
In Windows 8.1, go to the Start screen, type the word troubleshooting and click or tap the search result with the same name.
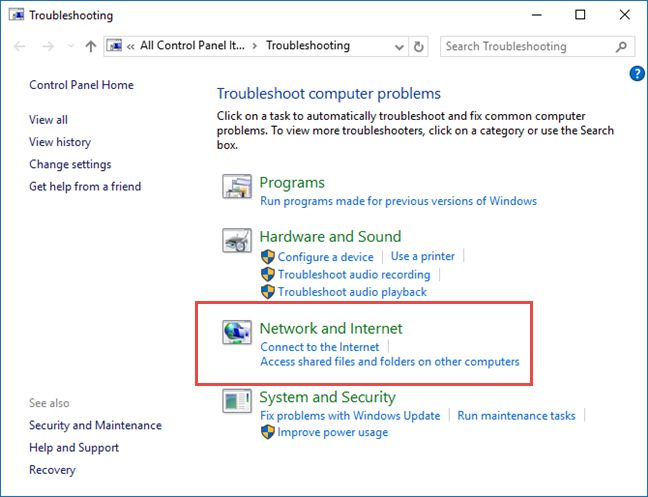
Clicking or tapping the Troubleshooting search result reveals the Troubleshooting window, where you find all the troubleshooting tools that are included in Windows. To display the troubleshooting wizards you are interested in, click or tap Network and Internet .
Now start the troubleshooting wizard that interests you. If you don't know what each wizard does, read the next section of this tutorial.
The network and internet troubleshooting wizards and what they do
You can start any of the available wizards, depending on the problem you are facing:
- Internet Connections - this wizard helps when you are connected to the network but the internet doesn't work or you have trouble accessing particular websites;
- Shared Folders - use this wizard when you have problems accessing shared files and folders on other computers and devices from your network;
- HomeGroup - when you have problems viewing computers or shared folders that are part of the Homegroup, use this wizard;
- Network Adapter - it is useful when you have problems with your wireless or wired network adapters. It helps with anything that is related to your network connection;
- Incoming Connections - this wizard is helpful when other computers have trouble connecting to your computer's shared files and folders;
- Connection to a Workplace Using DirectAccess - this wizard can be used when you have problems connecting to enterprise network domains. It is available only in Windows 7 Ultimate, Windows 7 Enterprise, Windows 8.1 Enterprise and Windows 10 Enterprise.
How to start the network and internet troubleshooting wizards from the Command Prompt
The network and internet troubleshooting wizards can also be started using the Command Prompt or the Run window. Execute the following commands inside the Command Prompt or the Run window:
- To open the Internet Connections troubleshooting wizard: msdt.exe -id NetworkDiagnosticsWeb ;
- To open the Shared Folders troubleshooting wizard: msdt.exe -id NetworkDiagnosticsFileShare ;
- To open the HomeGroup troubleshooting wizard: msdt.exe -id HomeGroupDiagnostic ;
- To open the Network Adapter troubleshooting wizard: msdt.exe -id NetworkDiagnosticsNetworkAdapter ;
- To open the Incoming Connections troubleshooting wizard: msdt.exe -id NetworkDiagnosticsInbound .
How to use the network and internet troubleshooting wizards in Windows
Each troubleshooting wizard is different because it solves only the problems it's designed to solve . To help you understand how to use a troubleshooting wizard, we ran the Network Adapter wizard in order to understand what is wrong with our network connection. Using other wizards works the same way, using the same principles.
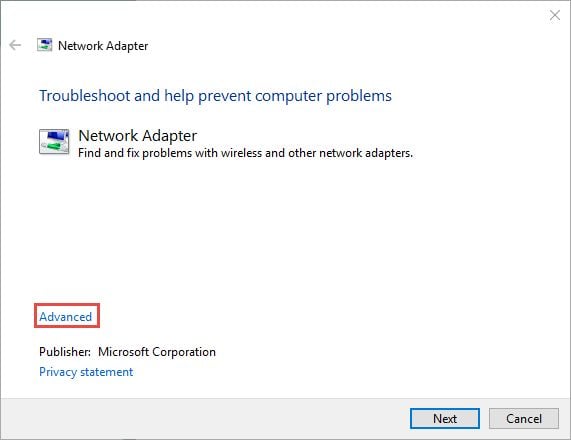
At the beginning of the troubleshooting wizard, before you press Next look for a link named Advanced .
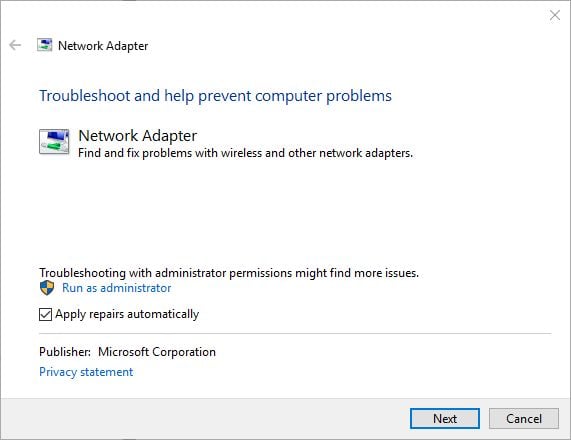
Click or tap on it. This reveals some interesting options. For example, the Network Adapter wizard can automatically apply repairs and run as administrator. Check the appropriate box to enable this feature and have it run as administrator, if you want to. Then, click or tap Next .
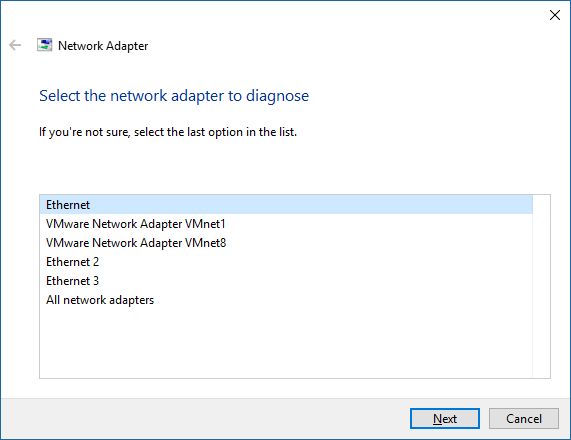
The troubleshooting wizard detects all network adapters that are installed on your Windows computer or device and asks you to select the one you want to troubleshoot. You can also have it troubleshoot all network adapters. Once you are done making your choice, click or tap Next .
NOTE: The Network Adapter troubleshooting wizard also displays virtual network adapters, if you have installed virtualization software that uses such devices (like VMWare, VirtualBox, etc).
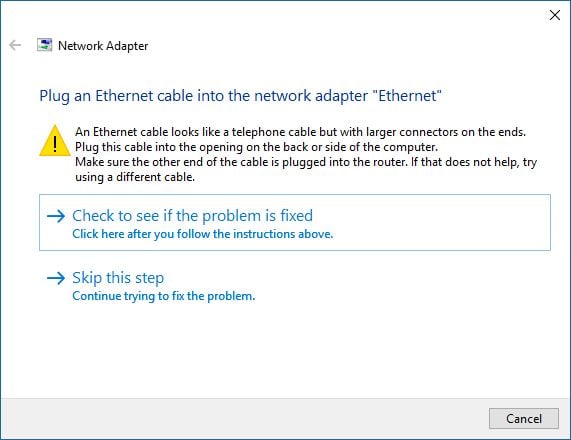
The troubleshooting wizard starts the diagnostics process and displays a progress bar. When it detects problems, it also tries to apply the fixes it believes are appropriate and then verifies if the problem still exists. For some problems, it may require you to perform a certain action. In our example, it detected that our network cable is not plugged at one end . So we verified the network cable, plugged it in, and then pressed "Check to see if the problem is fixed" .
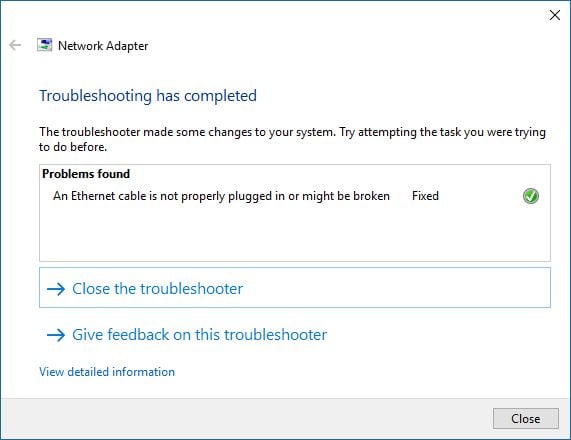
Then, it verifies whether the problem still persists and it sh ows you the details about the problem and its status.
If your problem remains unfixed, the Network Adapter wizard proposes additional options via the "Explorer additional options" button. If you want to view detailed information about the problem(s) it identified and what it has done to fix things, click the small link that says "View detailed information" . To close the wizard, press Close .
NOTE: If the troubleshooting wizard you have used hasn't detected any problems but you still have issues, you may have not used the correct wizard. In this case, try another troubleshooting wizard, which is better related to the problem that you are experiencing.
Troubleshooting problems with a wireless network
If you have troubles connecting to wireless networks, we recommend reading the following troubleshooting guides:
- Troubleshoot Internet Connection Problems over a Wireless Network - this guide shows how to use the Windows built-in troubleshooting tools, to fix problems when connecting to wireless networks;
- Troubleshoot Wireless Network Connection Problems by Yourself - this is a step by step chart with questions and answers. Answering a series of questions takes you to the most probable root-cause and its solution;
- The Layman's Guide to Solving Wireless Network Interference Problems - an awesome guide, sharing how easy it is to fix problems generated by the signal interference, caused by other networks in your area or by other devices.
- How to delete or forget wireless network profiles in Windows 10 - if the configuration of a wireless network has changed, it is a good idea to make Windows forget it so that you can start over and connect to it from scratch.
- How to reset all your Windows 10 network adapters with just 6 clicks - when your internet connection doesn't want to work and every troubleshooting idea you had seems to fail, a last resort action you can take is to reset your network adapter(s).
Conclusion
All modern versions of Windows provide a complete set of troubleshooting wizards which can help you identify the root cause of your networking problems. When we have issues, we use these wizards and, in most s ituation s , they are able to identify the root cause and give us useful recommendations.
Even when they cannot help fix the problems we encounter, they provide information that is valuable to the technical support staff that can fix things for us.


 19.10.2016
19.10.2016