Windows 11 used to have a Battery saver, and it still does, even though you may no longer find it. That’s because, starting with Windows 11 version 24H2, Battery Saver has turned into Energy saver. While the name of this feature has been changed, it works almost the same way it did in older versions of Windows 11. However, Microsoft wanted to emphasize that Energy saver extends battery life while also reducing energy usage. Moreover, it does that even on desktop computers, not just laptops and other devices with a battery. If you want to make Windows 11 use less power, here’s what Energy saver does, how to turn it on, how to change the way it works, and how to turn it off when you no longer need it:
How to turn on Energy saver in Windows 11
Energy saver can be manually turned on any Windows 11 device, including laptops, 2-in-1s, and even on desktop PCs without a battery. The first step to enable it is clicking or tapping the Battery status icon in the system tray, on the right side of the Windows 11 taskbar, to open Quick Settings. Then, click or tap the Energy saver icon to enable this feature.
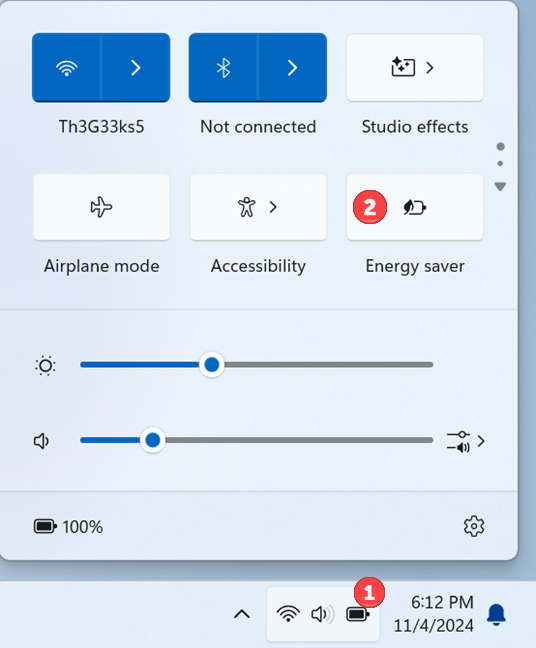
Enabling Energy saver on a Windows 11 laptop
If you’re on a desktop PC and don’t see the Battery status icon on your taskbar, you can also click or tap the Network or Speakers icon to open Quick Settings. On devices with a battery, Energy saver is displayed on the first page of Quick Settings. On a desktop PC, you usually find it on the second page.
TIP: If you want to change which icons you see on the taskbar, here’s how to add or remove icons or apps from the Windows 11 taskbar.
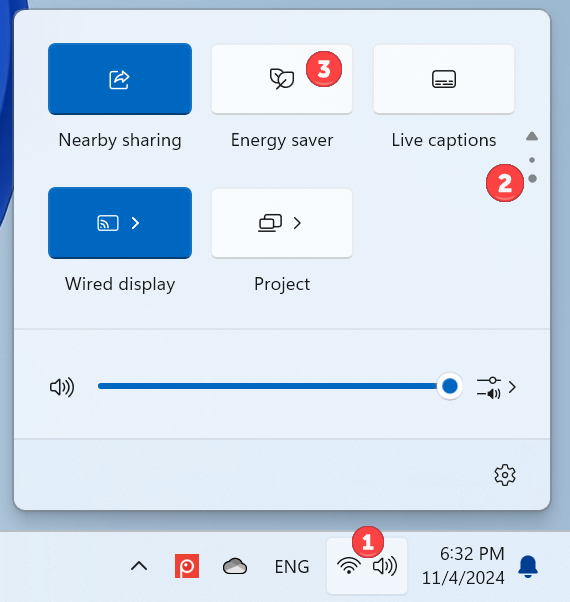
Enabling Energy saver on a desktop PC with Windows 11
You can also turn on Energy saver from the Settings app. To do that, first, open Windows 11 Settings (Windows + I) and navigate to System > Power (on desktop PCs) or System > Power & battery (on laptops and other devices with a battery). Next, click or tap Energy saver to extend this section of settings, and then click or tap the Always use energy saver switch.
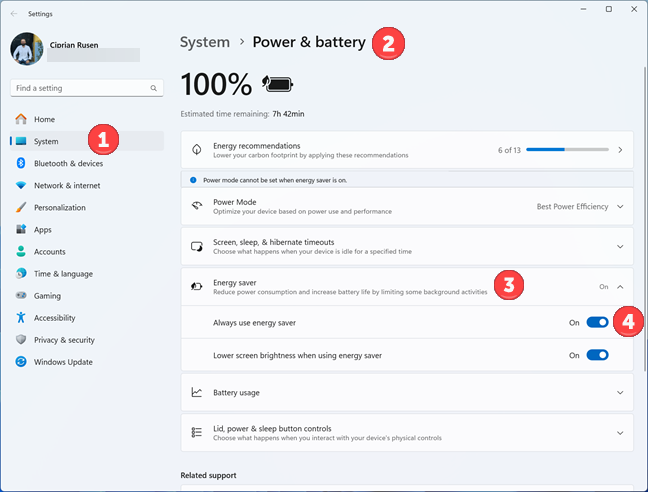
Enabling Energy saver from Windows 11 Settings
What does Windows 11 Energy saver do?
When you enable Energy saver in Windows 11, the Battery status icon in the system tray changes to include a leaf over the battery, signaling that your laptop or device is now running in an energy efficient way.
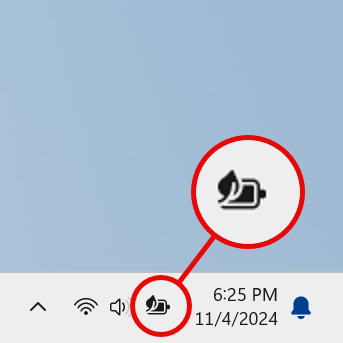
The Battery status icon with Energy saver turned On
Even though desktop computers don’t have a battery, a new icon shows up in the system tray, depicting two leaves. This signals that the Energy saver is turned on and doing its job.
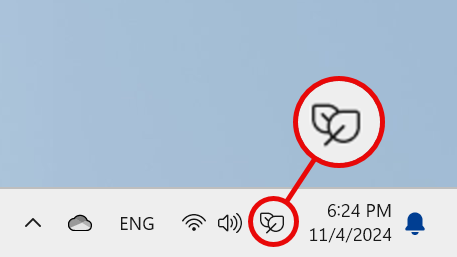
The Energy saver icon on desktop PCs
Aside from this minor visual difference, Energy saver does many things in the background to help your Windows 11 machine reduce power consumption and extend battery life. According to Microsoft’s technical documentation, here’s what it does:
- The display brightness is reduced by 30% (or another percentage set by the manufacturer of your device)
- Transparency effects on windows backgrounds are turned off
When your device is unplugged and low on battery, Energy saver also does the following:
- Microsoft apps like OneDrive, OneNote, and Phone Link stop synchronizing to reduce energy consumption.
- Apps running in the background are blocked. One notable exception to this rule is that Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) apps like Skype are not blocked.
- Non-critical Windows updates are blocked.
- Most Windows 11 telemetry is blocked. Only critical telemetry is allowed to be uploaded on Microsoft’s servers.
- Some scheduled tasks may not trigger and execute.
How to configure Energy saver in Windows 11
While you can turn on and turn off Energy saver at any time, you can also configure it to turn on automatically, like this:
Open Settings (Windows + I) and go to System > Power & battery. Then, click or tap the Energy saver section to extend it and display all its settings.
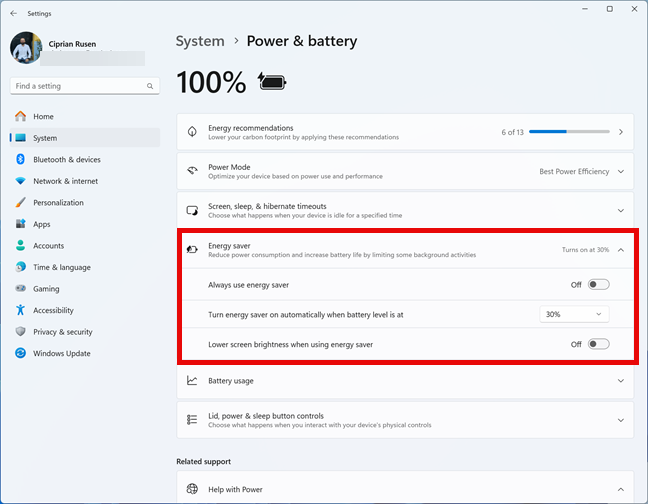
Accessing the settings for Windows 11 Energy saver
On laptops and devices with a battery, you can see three settings for Energy saver:
- Always use energy saver - it does what its name implies. Unless extending battery life is critical for you, you may not want this setting turned on at all times.
- Turn energy saver on automatically when battery level is at - the default battery level is 30%. However, you can click or tap the drop-down list next to it and choose another percentage from the list: Never, 10%, 20%, 40%, 50%, or Always.
- Lower screen brightness when using energy saver - turning this setting On is a good idea, because it doesn’t sacrifice screen visibility by a lot, and increases battery life.
On Windows 11 computers without a battery, only the first setting is available. The other two are missing.
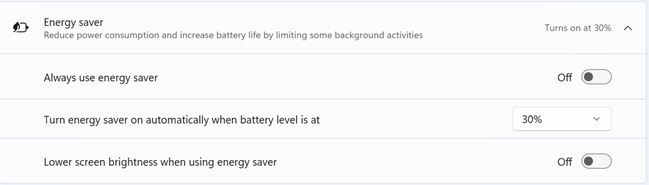
The settings available for Windows 11 Energy saver
I like the settings available for Energy Saver, but I consider Microsoft has missed something: offering a way for Energy saver to be turned off automatically when you plug your laptop into a power outlet or when the battery reaches a specific level.
How to turn off Energy saver in Windows 11
If you’re charging your laptop and no longer need the Energy saver, you can disable it like this: click or tap the Battery status icon in the bottom right corner of your taskbar and then the Energy saver button in Quick Settings. You can also open Settings, go to System > Power & battery, click or tap to expand Energy Saver, and turn off the Always use energy saver switch.
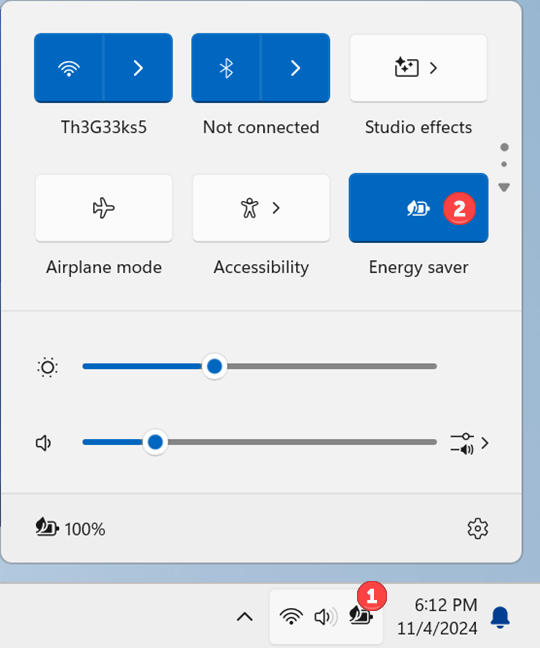
Disabling Energy saver in Windows 11
The Energy saver button is no longer highlighted, and the Battery status icon then loses the leaf. On a desktop computer, the two leaves icon disappears from the taskbar.
Do you use Energy saver to make Windows 11 use less power?
Now you know what Energy saver does in Windows 11 and how it helps your laptop, PC, or 2-in-1 device use less power and save battery. You also know why this feature was renamed from Battery saver to Energy saver, and how to customize it. Before closing this guide, I’m curious to learn what you think about Energy Saver and whether you consider it a useful feature. Also, is there anything you would like Microsoft to improve about the way it works? Comment using the options below, and let me know.


 05.11.2024
05.11.2024