DNS over HTTPS is one of the best new internet protocols designed to improve our security when browsing the web. It encrypts DNS lookups and helps in stopping third parties from snooping on your activities on the web. In the future, all the respectable browsers are probably going to enable DNS over HTTPS by default, but that is not the case right now. If you use Mozilla Firefox and want to turn on DNS over HTTPS, here's how to do it on your Windows PC and Android smartphone or tablet:
NOTE: In this tutorial, we show you how to enable DNS over HTTPS in Firefox for Windows and Android. Unfortunately, this feature is not yet available on iPhones. Also, if you don't know what DNS over HTTPS is, read: What is DNS over HTTPS or Secure DNS lookups? Enable it in Google Chrome!.
How to enable DNS over HTTPS in Firefox for Windows
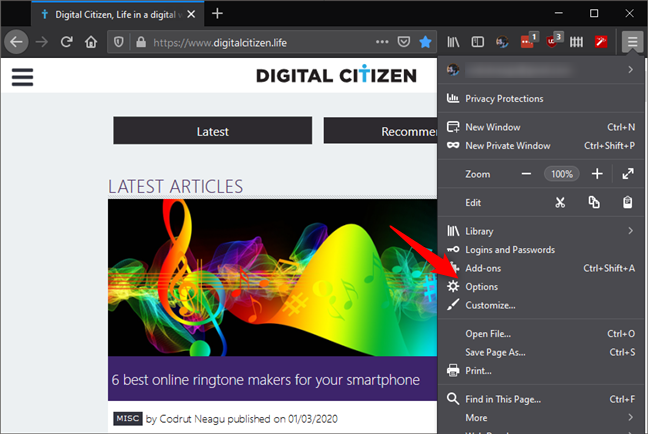
Enabling DNS over HTTPS in Firefox is easier than you might expect. Open Firefox on your Windows 10 PC and click or tap on its menu button. You can find it in Firefox's top-right corner.
In the menu, click or tap Options.
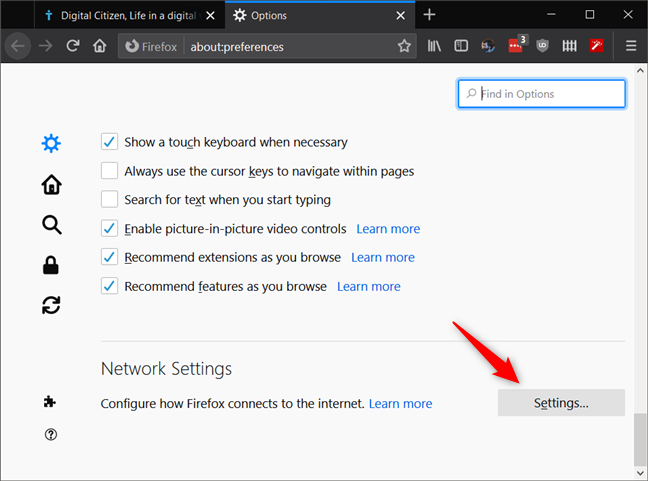
The Options tab is loaded. Scroll down until the end, where you should find a section called Network Settings. In it, there is a button called Settings: click or tap on it.
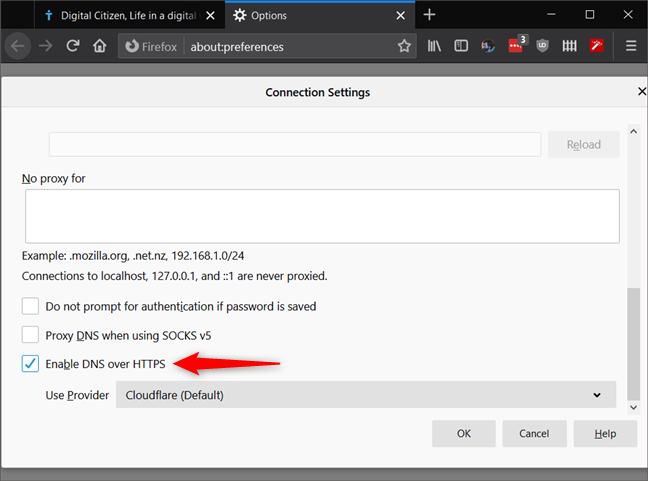
Now Firefox opens a dialog box named Connection Settings. To make Firefox use DNS over HTTPS, check the "Enable DNS over HTTPS" setting from the bottom of the dialog box.
Firefox uses Cloudflare for DNS over HTTPS, meaning that your DNS lookups are now sent to Cloudflare's DNS servers instead of the default DNS servers set by Windows 10 or by your router.
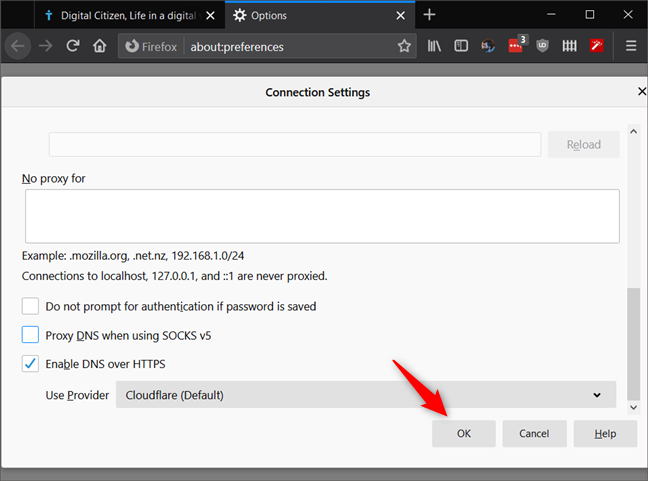
Click or tap on OK to save the changes, and close the Options tab.
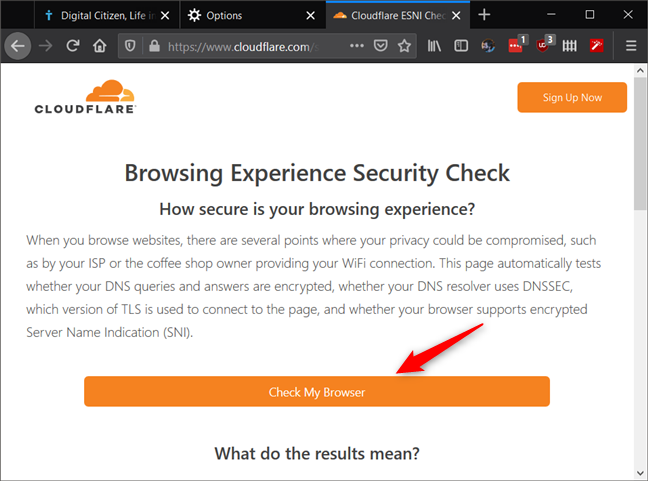
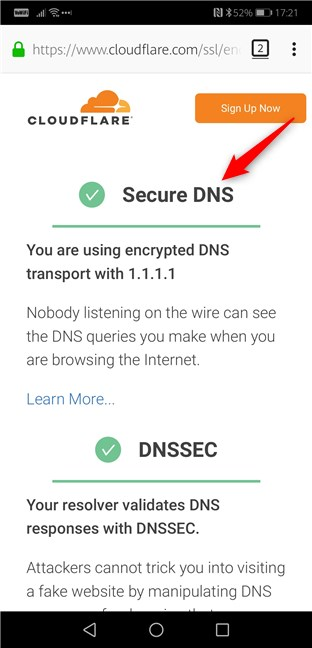
That was it! From now on, Firefox only makes secure DNS lookups. To check if everything works as it should, you can visit Cloudflare's Browsing Experience Security Check webpage. Click or tap on the "Check My Browser" button and wait for the testing to be done.
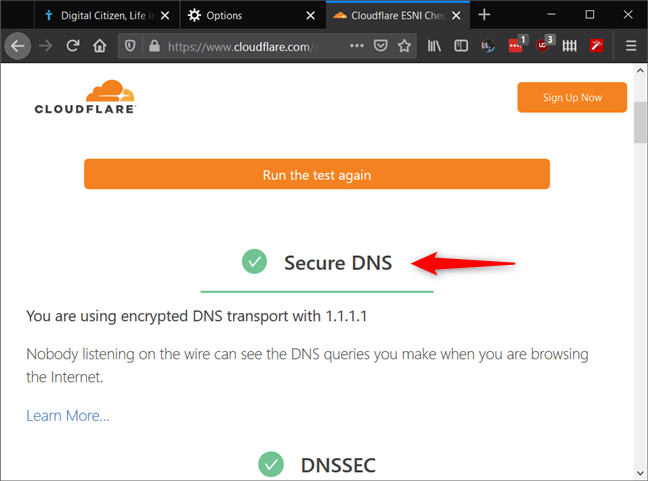
If the Secure DNS result is green and tells you that "You are using encrypted DNS transport with 1.1.1.1," then DNS over HTTPS is working correctly in your Firefox browser.
NOTE: Although the browser also allows you to add custom DNS over HTTPS providers, the process of doing so is too complex for regular users. On the other hand, you should know that, for Firefox to include other DNS over HTTPS providers on its list, they must abide by a strict set of rules, and right now only Cloudflare does, as the two companies have worked together on creating the DNS over HTTPS protocol. However, in December 2019, Mozilla announced that a second DNS over HTTPS provider is going to be included in its browser: NextDNS.
How to enable DNS over HTTPS in Firefox for Android
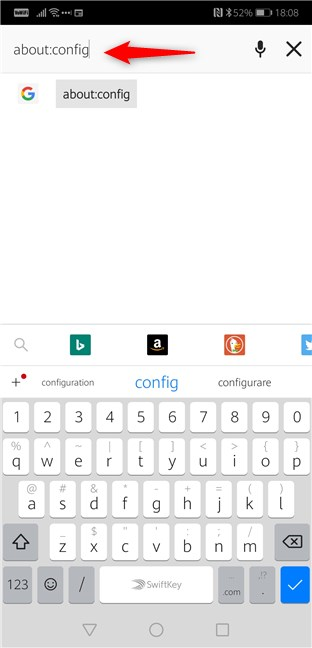
You can also enable DNS over HTTPS in Firefox for Android. However, unlike in Windows, Firefox for Android doesn't offer a setting that you can just turn on or off. In Android, open Firefox and use it to go to about:config.
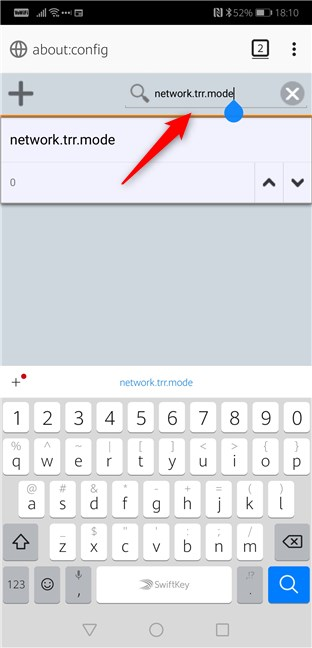
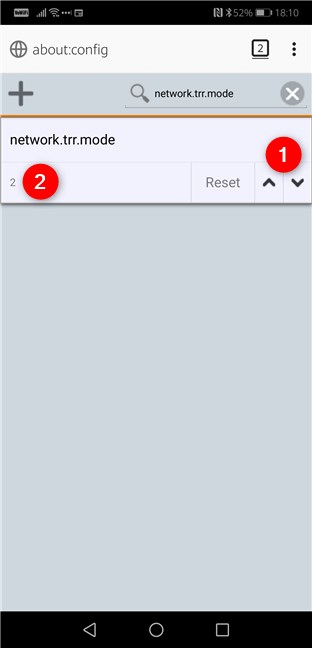
On the about:config page, type network.trr.mode in the Search field from the top-right corner.
You should see the network.trr.mode setting. By default, its value is set to 0 (zero). Use the arrow buttons on the right side of the setting to change its value to 2 (two). Once you do that, Firefox for Android starts using DNS over HTTPS based on Cloudflare's servers.
That's it! If you want to check if DNS over HTTPS is working in Firefox on your Android smartphone, visit Cloudflare's Browsing Experience Security Check webpage. Click or tap on the "Check My Browser" button, wait for the tests to end, and then check whether the Secure DNS result is highlighted green and tells you that "You are using encrypted DNS transport with 1.1.1.1".
Although the process doesn't look pretty, it gets the job done, and it is not complicated either.
Did you enable DNS over HTTPS in your Firefox browser?
Besides being an excellent measure for improving your online security, turning on DNS over HTTPS in Firefox is easier done than in other web browsers, such as Google Chrome. Did you enable DNS over HTTPS in your Firefox? Why did you do it, and did you encounter any issues? Let us know in the comments section below.


 07.01.2020
07.01.2020