There are some cases in which you might want to disable Task Manager in Windows 10. There are also opposite situations, when you want to enable Task Manager, like when your computer was infected by malware that disabled the Task Manager. In such a case, every time you try to launch it, you only get a message saying that the "Task Manager has been disabled by your administrator." Regardless of your reasons, here are four different ways in which you can enable or disable Task Manager. You can choose to use our free TaskMgrED tool for enabling or disabling Task Manager, the Windows Registry (regedit), Command Prompt or PowerShell, or even by changing a local policy (GPO).
NOTE: To be able to disable the Task Manager in Windows 10, you need to be logged on as an administrator.
1. How to disable Task Manager using our TaskMgrEd tool
The easiest way to disable the Task Manager in Windows 10 is to use a tool that we made for you, called TaskMgrEd. Download TaskMgrEd using this link or the one at the end of this section. Save it somewhere on your Windows 10 PC, and then double-click on it.
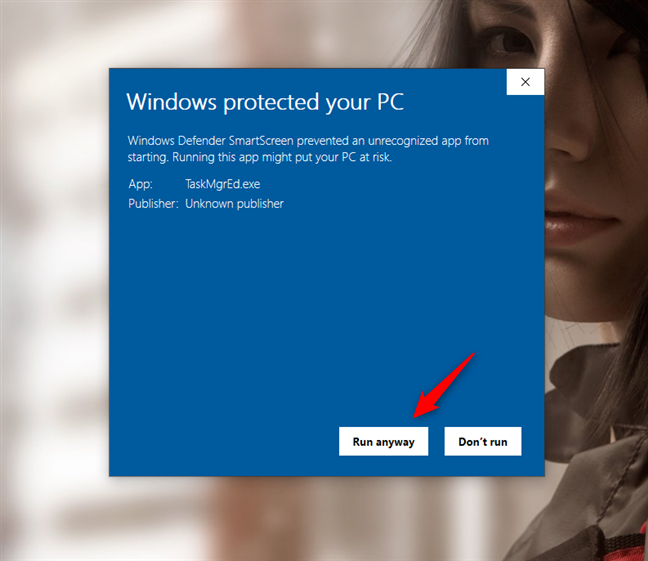
When you launch TaskMgrEd, the SmartScreen filter warns you that it comes from an untrusted publisher. You get this notification because it's a tool that we created, and there aren't that many people using it worldwide. The tool is safe and doesn't do any damage. It's just a script that we wrote in PowerShell, and we encapsulated it inside an executable file with a simple graphical user interface. To be able to use our tool, click or tap on "More info" and then choose to "Run anyway."
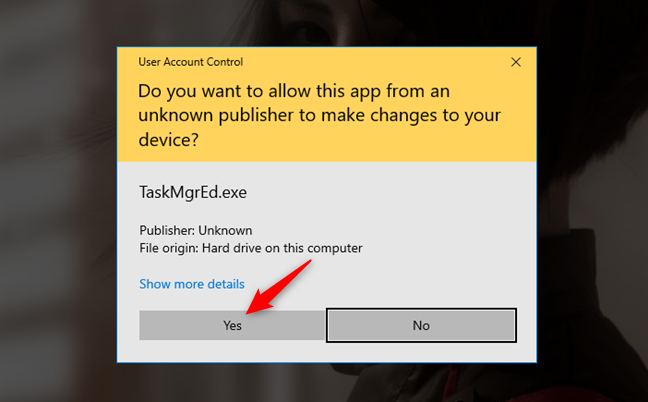
Each time you open TaskMgrEd, UAC asks you to run it as an administrator. Click or tap on Yes.
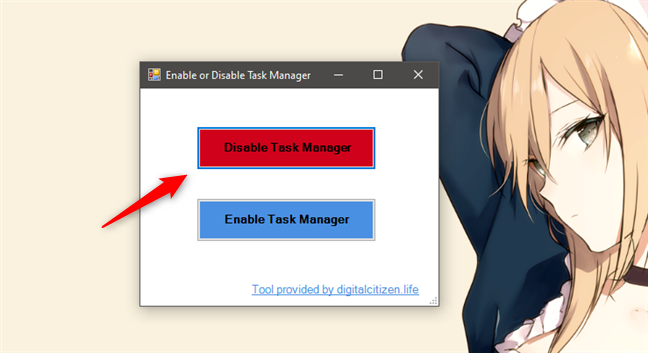
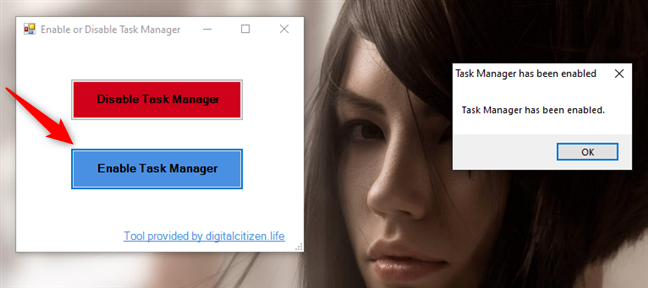
You should see a small window like the one illustrated in the image below. To disable the Task Manager on your Windows 10 PC, click or tap on "Disable Task Manager."
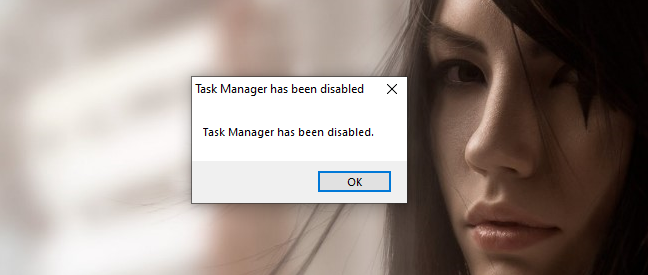
If all worked out well, you should see a message letting you know that "Task Manager has been disabled."
To enable or re-enable Task Manager on your Windows 10 computer, click or tap on "Enable Task Manager." TaskMgrEd should then inform you that "Task Manager has been enabled."
NOTE: Although we created this tool for Windows 10, it should also work on older Windows operating systems such as Windows 8.1, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and even Windows XP. If you encounter any issues with it, let us know via the comments section from the bottom of this article.
Download: TaskMgrED
2. How to disable Task Manager using the Windows Registry (regedit)
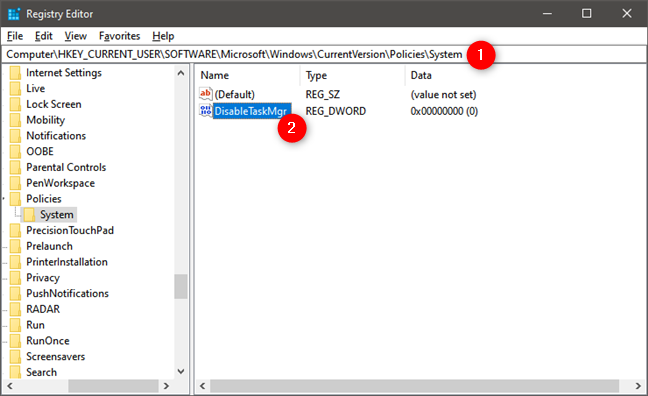
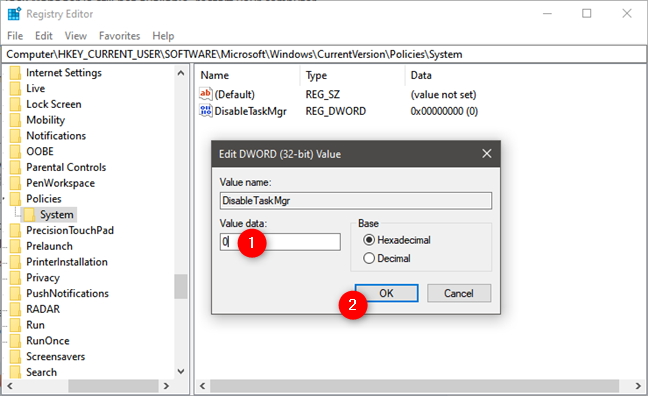
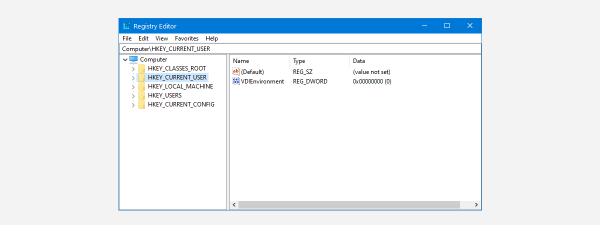
You can also use the Windows Registry if you want to disable the Task Manager. To do so, open regedit and navigate to this location: "Computer\HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System." Then, on the right side of the window, double-click to open the DisableTaskMgr property.
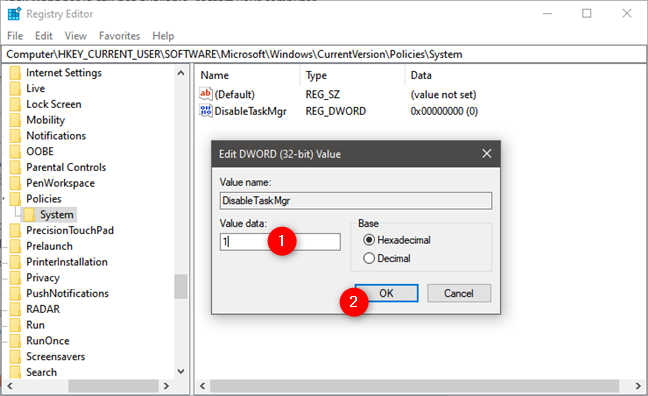
In the "Edit DWORD (32-bit) Value" window, set the "Value data" to 1 (one) and press the OK button if you want to disable Task Manager.
To enable Task Manager, follow the same path, and set the value of the DisableTaskMgr to 0 (zero).
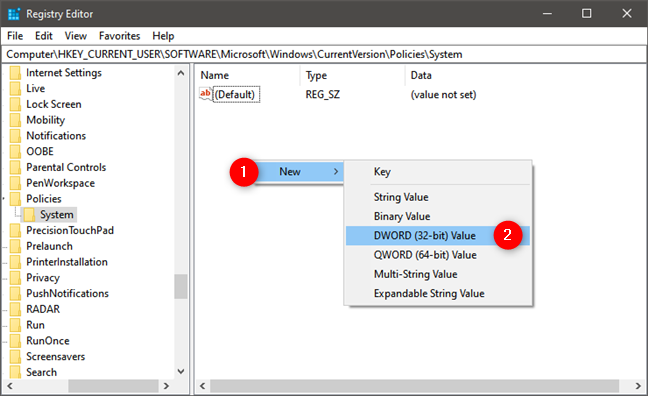
Note that, if you don't find the DisableTaskMgr item in your Windows Registry, you can and should create it yourself by using the right-click menu to create a new DWORD (32-bit) Value.
Just make sure that you type the correct name for the item: DisableTaskMgr.
3. How to disable Task Manager using Command Line (cmd) or PowerShell
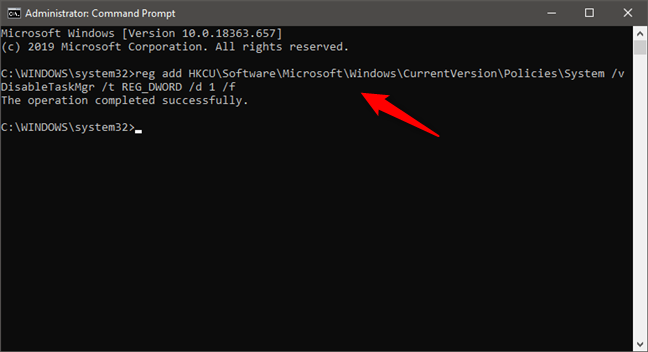
If you prefer using a command-line environment, open PowerShell, or Command Prompt as an administrator. Then, to disable Task Manager, run the following command: reg add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System /v DisableTaskMgr /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f.
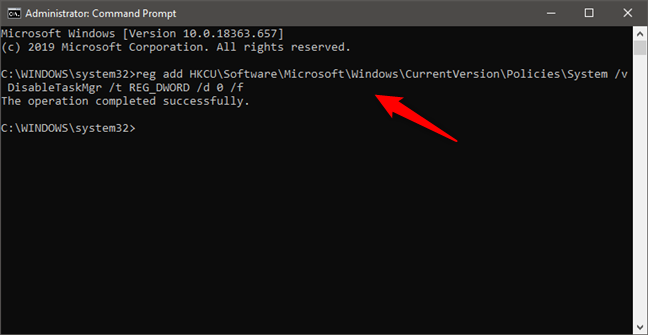
To enable Task Manager from Command Prompt run this command: reg add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System /v DisableTaskMgr /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f.
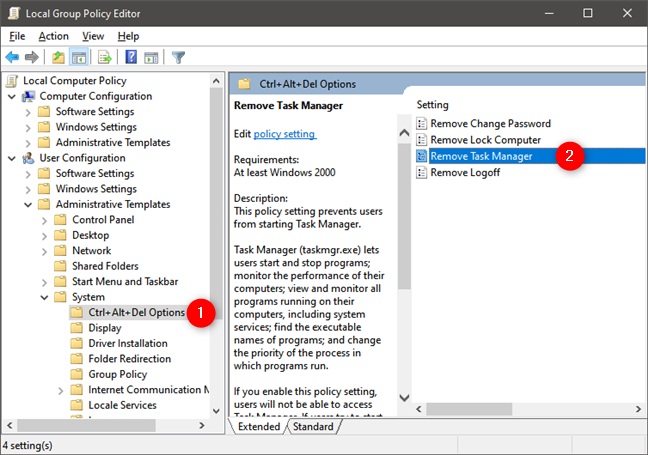
4. How to disable Task Manager using Local Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc)
If you're using Windows 10 Pro or Enterprise, you can also use local policies to enable or disable Task Manager. Open the Local Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc) and navigate to "User Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Ctrl+Alt+Del Options." Then, on the right side of the window, double-click or double-tap to open "Remove Task Manager."
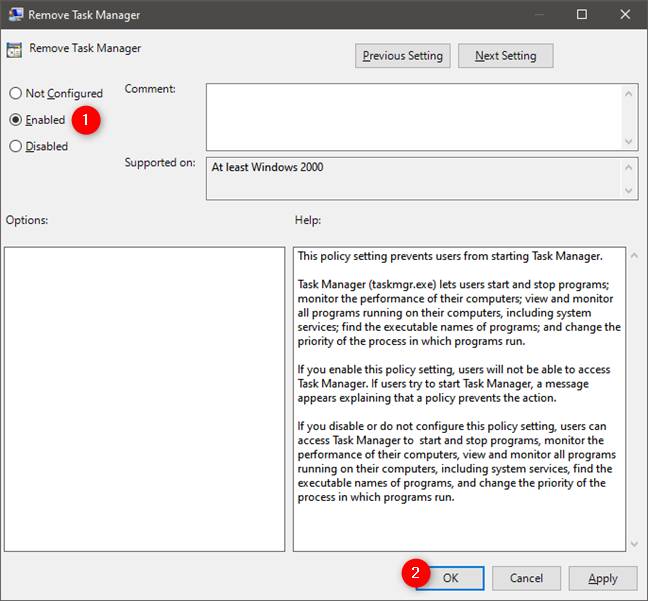
In the "Remove Task Manager" window, select Enabled and push OK or Apply if you want to disable Task Manager.
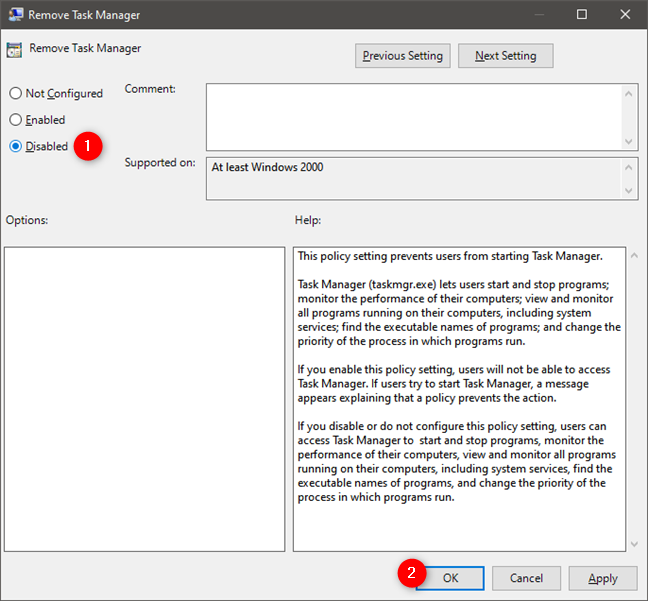
If what you want is to enable Task Manager, select Disabled or "Not configured" in the "Remove Task Manager" window and then save your choice by pushing OK or Apply.
TIP: For more about using the Local Group Policy Editor, read this guide: What is the Local Group Policy Editor, and how do I use it?.
What happens when you disable Task Manager in Windows 10?
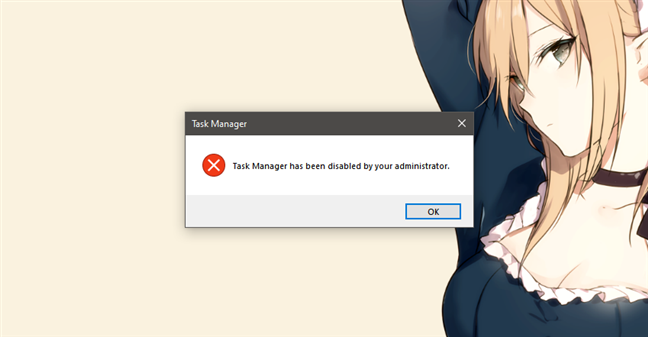
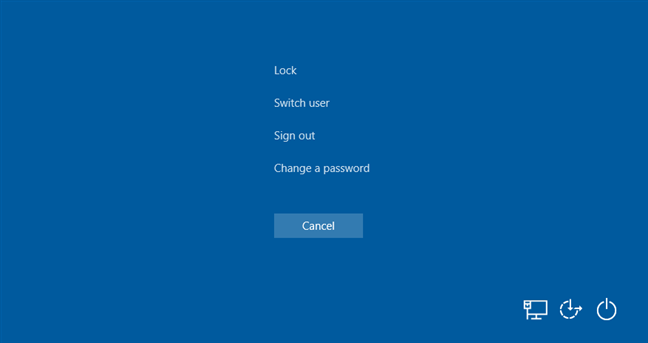
Regardless of the method you chose to disable it, if you try now to open the Task Manager using any of its shortcuts (like the one in the Start Menu) or using search, all you get is a message that tells you that the "Task Manager has been disabled by your administrator."
If you try to open it using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Shift + Esc, nothing happens. Furthermore, even the shortcut for Task Manager that used to be shown on the "Ctrl + Alt + Del" screen is gone.
That's it!
Why did you want to disable the Task Manager in Windows 10?
We're curious why you wanted to disable Task Manager on your Windows 10 computer? What was your reason for that? Or did you get to our article while looking for ways to re-enable Task Manager? You can reach us on this subject in the comments section below.


 24.02.2020
24.02.2020