I recently attended a press event where Cisco shared its 2024 Cybersecurity Readiness Index report. It gives an overview of the global cybersecurity landscape and evaluates how well-equipped organizations are to handle present-day cybersecurity risks. If you're interested in learning about the threats organizations face worldwide, the difficulties they encounter, and their readiness from a cybersecurity standpoint, I recommend reading this article. The report contains some intriguing statistics:
The dangers faced by organizations worldwide
According to the survey conducted by Cisco, 73% of respondents believe that their business is likely to face a cybersecurity incident in the next 12-24 months, which could lead to a major disruption. Being unprepared for such an eventuality can be costly, as 54% of respondents reported experiencing a cybersecurity incident in the past 12 months, and 52% of those affected incurred a cost of at least $300,000.
Over the past year, global organizations have faced a complex variety of attacks, including ransomware (35%), attacks targeting data and authentication processes (37%), supply chain attacks (32%), social engineering attacks (32%), and cryptojacking (27%). The situation is expected to continue evolving, with 11% of companies anticipating that AI-related cyber threats will be among the top three risks in the coming year.
How companies evaluate their cybersecurity
The Cybersecurity Readiness Index report highlighted some important findings:
- 80% of companies have a moderate to very high level of confidence in their ability to defend against a cyber attack with their current infrastructure.
- 46% of respondents said they had more than ten cybersecurity vacancies in their organization at the time of the survey.
- 80% of respondents admitted that having multiple solutions that address distinct needs has slowed their teams' ability to detect, react to, and recover from security incidents. This creates significant concerns, as 67% of organizations said they have implemented ten or more different solutions in their security architecture, while 25% said they have 30 or more solutions.
- 36% of companies consider identity protection to be their most difficult cybersecurity challenge.

The cybersecurity readiness of organizations worldwide
Some of the most important findings shared by Cisco
The confidence level reported by the companies that participated in the survey contrasts sharply with the findings of Cisco’s report. According to the assessments, only 3% of organizations globally have a Mature level of cybersecurity readiness - the level needed to withstand today's security risks. The report highlights that organizations' readiness has dropped significantly from a year ago, when 15% of companies were assessed as having a Mature level of readiness.
This difference between how confident organizations feel about their security readiness and their actual preparedness indicates that they may not effectively evaluate their own ability to handle cybersecurity threats and the extent of the challenges they may encounter. This discrepancy is particularly surprising considering the ongoing problem of skilled employee shortages, which has been highlighted by 87% of companies.
Many organizations are aware of the challenges of cybersecurity and are taking steps to improve their defenses. More than half of the companies surveyed (52%) plan to significantly upgrade their IT infrastructure within the next 12-24 months. This is a notable increase from just a third (33%) planning to do so last year. The majority of organizations (66%) plan to upgrade their existing solutions, 57% prepare to implement new solutions, and 55% intend to invest in artificial intelligence-based technologies. Additionally, 97% of companies aim to increase their cybersecurity budget in the next 12 months. Of those, 86% of respondents said their budgets would grow by 10% or more.
Artificial intelligence is part of the solution
In addition to the troubling data presented in the report, Cisco also provides useful recommendations for any organization, regardless of size or complexity:
- Organizations must continue to accelerate their investment in cybersecurity safeguards across the board, including adopting a platform-oriented approach, to ensure that all solutions in the security stack can be leveraged to their full capacity.
- It is important to promptly identify and eliminate any vulnerabilities created by unmanaged devices and unsecured Wi-Fi networks used by employees.
- Adopting generative AI technology and leveraging it to improve security programs and operational resilience.
- Intensifying the recruitment and training of specialists to reduce the cybersecurity talent shortage. Where possible, leverage advances in artificial intelligence to enhance and automate workloads while drawing in external cybersecurity expertise to help address key gaps in building and operating cybersecurity infrastructure.
- Establishing a baseline of how prepared the organization is in terms of key security pillars, monitoring them on an ongoing basis, and taking concrete action in areas where needed.
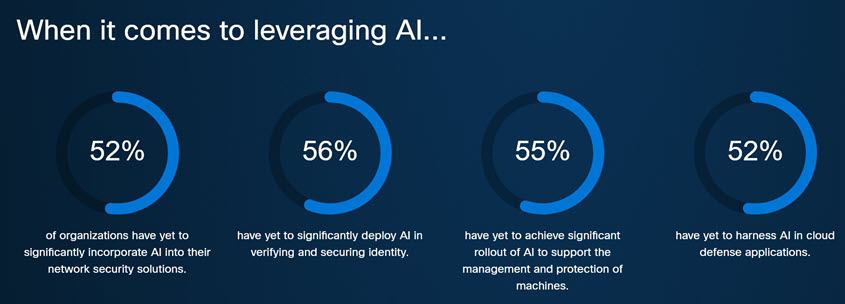
It is evident from the report that artificial intelligence is not only a threat to organizations worldwide but also an essential part of the solution. Unfortunately:
- 52% of organizations have not yet significantly incorporated artificial intelligence into their security solutions
- 56% have not implemented AI in their employee identity protection either
- 55% have not yet managed to significantly implement AI to support the management and protection of the devices they use
- 52% have not yet leveraged AI in applications to defend the cloud solutions they use.
The adoption of AI in cybersecurity
The 2024 Cybersecurity Readiness Index highlights the need to integrate artificial intelligence into cybersecurity platforms and reveals that global organizations, with small exceptions, are just starting to do so.
The methodology used for the Cisco Cybersecurity Readiness Index
The companies surveyed in the report were assessed using five key pillars for resilient cybersecurity in the face of modern threats:
- Identity Intelligence - an assessment of how a company protects the identity of its employees, network authentication mechanisms, and internal services. Advanced mechanisms are required to safeguard users and verify their identities, the contexts in which they log on to the network, and their access rights. These mechanisms are crucial to ensuring the protection of business networks in 2024.
- Machine Trustworthiness - Cisco assessed not only the diversity of devices used by employees within the company (laptops, phones, tablets, smartwatches, etc.) but also the smart devices used within the company (sensors, smart industrial machines, lock/unlock, surveillance cameras, etc.). All these devices can be a point of entry into the network for a malicious actor. Cisco has, therefore, assessed how all types of devices that access the network and the services, applications, and data within it are protected and managed.
- Network Resilience - a significant percentage of employees worldwide enjoy a hybrid work environment, working from a large number of locations outside the company and its network. This increases the complexity of the protection required so that company and employee data is not stolen by malicious actors. For the best protection, solutions are needed to analyze encrypted network traffic, firewalls with intrusion prevention systems, anomaly detection solutions for network traffic, etc.
- Cloud Reinforcement - many organizations are using cloud solutions managed by third parties or hybrid cloud solutions. These come with additional security challenges and specialized protection tools are needed, such as software firewalls and the implementation of secure access perimeters to these services.
- AI Fortification - a growing number of malicious actors use artificial intelligence tools to overcome and compromise business organizations' cyber defense shields. Cisco has assessed the level of adoption of AI technologies in the security tools organizations use to increase the effectiveness of their protection.
For each key area, an importance score was assigned, and depending on the answers given, each organization was rated up to a maximum of 100. Companies were then categorized into four stages of readiness development: Beginner, Formative, Progressive, and Mature.
Download the Cisco Cybersecurity Readiness Index
The report includes plenty of interesting data, including a detailed description of the methodology used, as well as useful recommendations on how individual organizations can fortify their security. One of the most interesting things in Cisco's assessment is the split by business sectors, which shows which types of organizations tend to be more mature in their approach to cybersecurity, which don't, and why. For example, there are consistent differences between companies providing business services and those in the education sector. And the companies that seem to have most readily understood the need for artificial intelligence fortification are those in the technology sector. If I made you curious, you can access the full report here: 2024 Cisco Cybersecurity Readiness Index.


 29.04.2024
29.04.2024